ClC-3 chloride channel modulates the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells via AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway
- PMID: 25973047
- PMCID: PMC4396317
ClC-3 chloride channel modulates the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells via AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway
Abstract
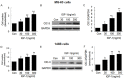
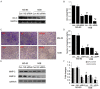
In cultured human osteosarcoma (OS) cells, we recently demonstrated that insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1)-induced MG-63 and 143B human OS cells proliferation were consistent with increasing ClC-3 expression, and ClC-3 was up-regulated in cells with high metastatic potency. Blockade of ClC-3 greatly suppressed the phosphorylation activation of Akt/GSK3β. We also found that blockade of ClC-3 effectively down-regulated the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E, and caused activation of p27(KIP) and p21(CIP). The synthesized effects on these proteins which play a major role in cell cycle regulation bring about G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in MG-63 cells, and finally abrogate the cell proliferation. Besides, ClC-3 deletion attenuates OS cell migration via down-regulation the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Such information suggests that ClC-3 might be a potential target for anti-OS.
Keywords: AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway; ClC-3 chloride channel; osteosarcoma; proliferation and migration.
Figures


References
-
- Guan YY, Wang GL, Zhou JG. The ClC-3 Cl-channel in cell volume regulation, proliferation and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:290–296. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Wu DB, Wang J. Effects of volume-activated chloride channels on the invasion and migration of human endometrial cancer cells. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2013;34:60–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
