Membranous expressions of Lewis y and CAM-DR-related markers are independent factors of chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 25973320
- PMCID: PMC4396026
Membranous expressions of Lewis y and CAM-DR-related markers are independent factors of chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy resistance is a common problem faced by patients diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Currently there are no specific or sensitive clinical biomarkers that maybe implemented to identify chemotherapy resistance and give insight to prognosis. The aim of this study is to investigate the roles of Lewis y antigen and the markers associated with cell-adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) in patients with EOC.
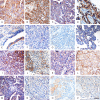
Methods: 92 EOC patients who were treated with systemic chemotherapy after cytoreductive surgery were included in this analysis. Patients were divided into two groups, chemotherapy sensitive (n = 56) and resistant (n = 36). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for Lewis y and CAM-DR-related cell surface proteins including CD44, CD147, HE4 (Human epididymis protein 4), integrin α5, β1, αv and β3 were conducted on tissues collected during primary debulking surgery. Using multivariate logistic regressions, IHC results were compared to clinical variables and chemotherapy resistance to determine possible correlations. The relationships between IHC expression and progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression analysis.
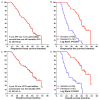
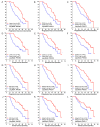
Results: Membranous expression of Lewis y and all these CAM-DR-related markers were significantly higher in the resistant group than that of the sensitive group (all P < 0.01). Multivariate regression analysis revealed that high expression of Lewis y, CD44, HE4, integrin α5 and β1 as well as advanced FIGO stage were independent risk factors for chemotherapy resistance (all P < 0.05). Advanced FIGO stage, lymph node metastasis and high expression of Lewis y, CD44, CD147, HE4, integrin α5, β1 were associated with a shorter PFS and OS (all P < 0.05). Moreover, multivariate COX analysis demonstrated that the following variates were independent predictors of worse PFS and OS survival: late FIGO stage (P = 0.013, 0.049), high expressions of Lewis y (P = 0.010, 0.036), HE4 (P = 0.006, 0.013) and integrin β1 (PFS, P = 0.003), integrin α5 (OS, P = 0.019).
Conclusion: Membranous expression of Lewis y and CAM-DR-related markers including CD44, CD147, HE4, integrin α5, β1, αv and β3 are associated with the development of chemotherapy resistance. High expression of Lewis y antigen and CAM-DR-related markers including CD44, CD147, HE4, integrin α5 and β1 are independent markers for PFS and OS, in which Lewis y and HE4 are the most significant.
Keywords: CAM-DR; Epithelial ovarian cancer; HE4; Lewis y; chemotherapy resistance; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Pliarchopoulou K, Pectasides D. Epithelial ovarian cancer: focus on targeted therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;79:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:714–726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
