Imaging modality utilization trends in patients with stage III-IV oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25973336
- PMCID: PMC4396006
Imaging modality utilization trends in patients with stage III-IV oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
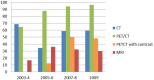
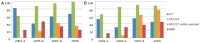
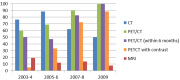
The objective of this study is to establish the utilization trends of CT, MRI, and FDG-PET/CT for evaluation of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) patients. A total of 173 patients with newly diagnosed stage III or IV OPSCC between 2003 and 2009 were included. Frequency of imaging modality use, divided into four time periods (2003-04, 2005-06, 2007-08 and 2009), was evaluated. For initial staging, percentage of PET/CT use was 64.6%, 87.5%, 94.1% and 96.3%, with an increasing trend (p < 0.001). The CT (p = 0.762) and MRI (p = 0.224) use demonstrated no change in trend. For post-treatment imaging, percentage of PET/CT use was 59.5%, 68.6%, 89.7% and 100%, with an increasing trend (p < 0.001). The CT use demonstrated a decreasing trend (p = 0.004) and MRI showed no trend change (p = 0.231). PET/CT is used with an increasing trend for initial staging and has become a central imaging modality for follow up evaluation after treatment, for advanced OPSCC.
Keywords: FDG; Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC); PET/CT; cancer; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
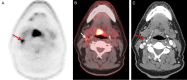
Figures
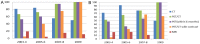
References
-
- American Cancer Society. What are the key statistics about oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Accessed on 23th March, 2013.
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Head and Neck Cancers version1. 2012.
-
- Hammarstedt L, Lindquist D, Dahlstrand H, Romanitan M, Dahlgren LO, Joneberg J, Creson N, Lindholm J, Ye W, Dalianis T, Munck-Wikland E. Human papillomavirus as a risk factor for the increase in incidence of tonsillar cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:2620–2623. - PubMed
-
- Poeppel TD, Krause BJ, Heusner TA, Boy C, Bockisch A, Antoch G. PET/CT for the staging and follow-up of patients with malignancies. Eur J Radiol. 2009;70:382–392. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
