Prospects for malaria elimination in Mesoamerica and Hispaniola
- PMID: 25973753
- PMCID: PMC4431857
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003700
Prospects for malaria elimination in Mesoamerica and Hispaniola
Abstract
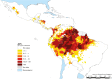
Malaria remains endemic in 21 countries of the American continent with an estimated 427,000 cases per year. Approximately 10% of these occur in the Mesoamerican and Caribbean regions. During the last decade, malaria transmission in Mesoamerica showed a decrease of ~85%; whereas, in the Caribbean region, Hispaniola (comprising the Dominican Republic [DR] and Haiti) presented an overall rise in malaria transmission, primarily due to a steady increase in Haiti, while DR experienced a significant transmission decrease in this period. The significant malaria reduction observed recently in the region prompted the launch of an initiative for Malaria Elimination in Mesoamerica and Hispaniola (EMMIE) with the active involvement of the National Malaria Control Programs (NMCPs) of nine countries, the Regional Coordination Mechanism (RCM) for Mesoamerica, and the Council of Health Ministries of Central America and Dominican Republic (COMISCA). The EMMIE initiative is supported by the Global Fund for Aids, Tuberculosis and Malaria (GFATM) with active participation of multiple partners including Ministries of Health, bilateral and multilateral agencies, as well as research centers. EMMIE's main goal is to achieve elimination of malaria transmission in the region by 2020. Here we discuss the prospects, challenges, and research needs associated with this initiative that, if successful, could represent a paradigm for other malaria-affected regions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have decared that no competing interest exist.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (2014) World Malaria Report 2014 Geneva: WHO. 219 p.
-
- Roll Back Malaria Partnership (2012) Roll Back Malaria Partnership Annual Report 2012 Roll Back Malaria.
-
- Pan American Health Organization (2014) Malaria Surveillance Indicators.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

