Brucella spp. Lumazine Synthase Induces a TLR4-Mediated Protective Response against B16 Melanoma in Mice
- PMID: 25973756
- PMCID: PMC4431812
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126827
Brucella spp. Lumazine Synthase Induces a TLR4-Mediated Protective Response against B16 Melanoma in Mice
Abstract
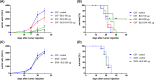
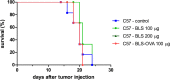
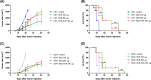
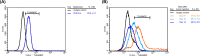
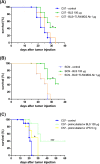
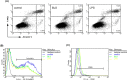
Brucella Lumazine Synthase (BLS) is a highly immunogenic decameric protein which can accept the fusion of foreign proteins at its ten N-termini. These chimeras are very efficient to elicit systemic and oral immunity without adjuvants. BLS signaling via Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) regulates innate and adaptive immune responses, inducing dendritic cell maturation and CD8(+) T-cell cytotoxicity. In this work we study the effect induced by BLS in TLR4-expressing B16 melanoma. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of BLS as a preventive vaccine, C57BL/6J mice were immunized with BLS or BLS-OVA, and 35 days later were subcutaneously inoculated with B16-OVA melanoma. BLS or BLS-OVA induced a significant inhibition of tumor growth, and 50% of mice immunized with the highest dose of BLS did not develop visible tumors. This effect was not observed in TLR4-deficient mice. For treatment experiments, mice were injected with BLS or BLS-OVA 2 days after the inoculation of B16 cells. Both treatments induced significant and equal tumor growth delay and increased survival. Moreover, BLS and BLS-OVA stimulation were also effective in TLR4-deficient mice. In order to study whether BLS has a direct effect on tumor cells, B16 cells were preincubated with BLS, and after 48h, cells were inoculated. Tumors induced by BLS-stimulated cells had inhibited growth and survival was increased. In the BLS group, 40% of mice did not develop tumors. This effect was abolished by the addition of TLR4/MD2 blocking antibody to cells before BLS stimulation. Our work demonstrates that BLS immunization induces a preventive antitumor response that depends on mice TLR4. We also show that BLS generates a therapeutic effect in mice inoculated with B16 cells. Our results show that BLS acts directly in cultured tumor cells via TLR4, highly suggesting that BLS elicits its therapeutic effects acting on the TLR4 from B16 melanoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of structural and immunological properties of a fusion protein between flagellin from Salmonella and lumazine synthase from Brucella.Protein Sci. 2017 May;26(5):1049-1059. doi: 10.1002/pro.3151. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28257593 Free PMC article.
-
A polymeric protein induces specific cytotoxicity in a TLR4 dependent manner in the absence of adjuvants.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045705. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029192 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of antitumor immunity through anti-MICA antibodies elicited with a chimeric protein.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Jun;8(1):e000233. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000233. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32518090 Free PMC article.
-
Brucella spp. lumazine synthase as a bovine rotavirus antigen delivery system.Vaccine. 2009 Jan 1;27(1):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.10.018. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 18973781
-
Recombinant E. coli LLO/OVA induces murine BMDCs maturation via TLR4 and NOD1 receptor and promotes specific cytotoxic T cell immunity.Biomed Environ Sci. 2010 Oct;23(5):350-6. doi: 10.1016/S0895-3988(10)60075-X. Biomed Environ Sci. 2010. PMID: 21112482
Cited by
-
Improvement of Cellulomonas fimi endoglucanase CenA by multienzymatic display on a decameric structural scaffold.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(13):4261-4274. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12581-6. Epub 2023 May 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37212884 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of structural and immunological properties of a fusion protein between flagellin from Salmonella and lumazine synthase from Brucella.Protein Sci. 2017 May;26(5):1049-1059. doi: 10.1002/pro.3151. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28257593 Free PMC article.
-
A TLR4 agonist improves immune checkpoint blockade treatment by increasing the ratio of effector to regulatory cells within the tumor microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 28;11(1):15406. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94837-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34321536 Free PMC article.
-
Aloin promotes cell apoptosis by targeting HMGB1-TLR4-ERK axis in human melanoma cells.EXCLI J. 2020 May 14;19:641-651. eCollection 2020. EXCLI J. 2020. PMID: 32536835 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immune Response to Powassan Virus Infection: Progress Toward Infection Control.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jul 15;13(7):754. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13070754. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schreibelt G, Tel J, Sliepen KH, Benitez-Ribas D, Figdor CG, Adema GJ, et al. Toll-like receptor expression and function in human dendritic cell subsets: implications for dendritic cell-based anti-cancer immunotherapy. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy: CII. 2010;59(10):1573–82. Epub 2010/03/06. 10.1007/s00262-010-0833-1 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asprodites N, Zheng L, Geng D, Velasco-Gonzalez C, Sanchez-Perez L, Davila E. Engagement of Toll-like receptor-2 on cytotoxic T-lymphocytes occurs in vivo and augments antitumor activity. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2008;22(10):3628–37. Epub 2008/07/01. 10.1096/fj.08-108274 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

