Characterization of a Single-Stranded DNA-Binding-Like Protein from Nanoarchaeum equitans--A Nucleic Acid Binding Protein with Broad Substrate Specificity
- PMID: 25973760
- PMCID: PMC4431734
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126563
Characterization of a Single-Stranded DNA-Binding-Like Protein from Nanoarchaeum equitans--A Nucleic Acid Binding Protein with Broad Substrate Specificity
Abstract
Background: SSB (single-stranded DNA-binding) proteins play an essential role in all living cells and viruses, as they are involved in processes connected with ssDNA metabolism. There has recently been an increasing interest in SSBs, since they can be applied in molecular biology techniques and analytical methods. Nanoarchaeum equitans, the only known representative of Archaea phylum Nanoarchaeota, is a hyperthermophilic, nanosized, obligatory parasite/symbiont of Ignicoccus hospitalis.
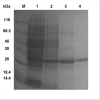
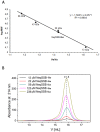
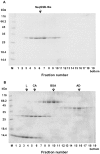
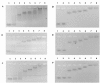
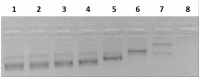
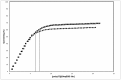
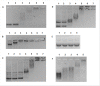
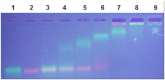
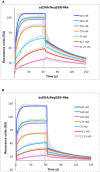
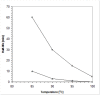
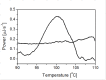
Results: This paper reports on the ssb-like gene cloning, gene expression and characterization of a novel nucleic acid binding protein from Nanoarchaeum equitans archaeon (NeqSSB-like protein). This protein consists of 243 amino acid residues and one OB fold per monomer. It is biologically active as a monomer like as SSBs from some viruses. The NeqSSB-like protein displays a low sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli SSB, namely 10% identity and 29% similarity, and is the most similar to the Sulfolobus solfataricus SSB (14% identity and 32% similarity). The NeqSSB-like protein binds to ssDNA, although it can also bind mRNA and, surprisingly, various dsDNA forms, with no structure-dependent preferences as evidenced by gel mobility shift assays. The size of the ssDNA binding site, which was estimated using fluorescence spectroscopy, is 7 ± 1 nt. No salt-dependent binding mode transition was observed. NeqSSB-like protein probably utilizes a different model for ssDNA binding than the SSB proteins studied so far. This protein is highly thermostable; the half-life of the ssDNA binding activity is 5 min at 100 °C and melting temperature (T(m)) is 100.2 °C as shown by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis.
Conclusion: NeqSSB-like protein is a novel highly thermostable protein which possesses a unique broad substrate specificity and is able to bind all types of nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of single-stranded DNA-binding protein from the facultative psychrophilic bacteria Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis.Microbiol Res. 2014 Feb-Mar;169(2-3):139-47. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Microbiol Res. 2014. PMID: 23953921
-
Fusion of Taq DNA polymerase with single-stranded DNA binding-like protein of Nanoarchaeum equitans-Expression and characterization.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 1;12(9):e0184162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184162. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28863186 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of single-strand DNA-binding proteins in DNA replication, recombination, and repair.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;922:1-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-032-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22976174
-
Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein: multiple DNA-binding modes and cooperativities.Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:527-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002523. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7979247 Review.
-
Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Proteins in the Archaea.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2281:23-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1290-3_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33847950 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-stranded binding proteins and helicase enhance the activity of prokaryotic argonautes in vitro.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 29;13(8):e0203073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203073. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30157272 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of two key enzymes for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in symbiotic archaea.Extremophiles. 2016 Jul;20(4):503-14. doi: 10.1007/s00792-016-0840-z. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Extremophiles. 2016. PMID: 27290727
-
Sequence, genome organization, annotation and proteomics of the thermophilic, 47.7-kb Geobacillus stearothermophilus bacteriophage TP-84 and its classification in the new Tp84virus genus.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 6;13(4):e0195449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195449. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29624616 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and procedures to generate chimeric DNA polymerases for improved applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 21;108(1):445. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13276-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39167106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermostable proteins bioprocesses: The activity of restriction endonuclease-methyltransferase from Thermus thermophilus (RM.TthHB27I) cloned in Escherichia coli is critically affected by the codon composition of the synthetic gene.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 17;12(10):e0186633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186633. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29040308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huber H, Hohn MJ, Rachel R, Fuchs T, Wimmer VC, Stetter KO. A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont. Nature. 2002. May 2;417(6884):63–7. - PubMed
-
- Nakabachi A, Yamashita A, Toh H, Ishikawa H, Dunbar HE, Moran NA, et al. The 160-kilobase genome of the bacterial endosymbiont Carsonella . Science. 2006. October 13;314(5797):267 - PubMed
-
- Greipel J, Urbanke C, Maass G. The single-stranded DNA binding protein of Escherichia coli. Physicochemical properties and biological functions In: Saenger W, Heinemann U, editors. Protein-Nucleic Acid Interaction. London: Macmillan; 1989. p. 61–86.
-
- Alani E, Thresher R, Griffith JD, Kolodner RD. Characterization of DNA-binding and strand-exchange stimulation properties of y-RPA, a yeast single-strand-DNA-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1992. September 5;227(1):54–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

