Identifying Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque in Rabbits Using DMSA-USPIO Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Investigate the Effect of Atorvastatin
- PMID: 25973795
- PMCID: PMC4431872
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125677
Identifying Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque in Rabbits Using DMSA-USPIO Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Investigate the Effect of Atorvastatin
Abstract
Background: Rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque is the primary cause of acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular syndromes. Early and non-invasive detection of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques (VP) would be significant in preventing some aspects of these syndromes. As a new contrast agent, dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) modified ultra-small super paramagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) was synthesized and used to identify VP and rupture plaque by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods: Atherosclerosis was induced in male New Zealand White rabbits by feeding a high cholesterol diet (n = 30). Group A with atherosclerosis plaque (n = 10) were controls. VP was established in groups B (n = 10) and C (n = 10) using balloon-induced endothelial injury of the abdominal aorta. Adenovirus-carrying p53 genes were injected into the aortic segments rich in plaques after 8 weeks. Group C was treated with atorvastatin for 8 weeks. Sixteen weeks later, all rabbits underwent pharmacological triggering, and imaging were taken daily for 5 d after DMSA-USPIO infusion. At the first day and before being killed, serum MMP-9, sCD40L, and other lipid indicators were measured.
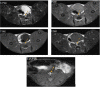
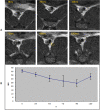
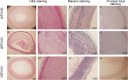
Results: DMSA-USPIO particles accumulated in VP and rupture plaques. Rupture plaques appeared as areas of hyper-intensity on DMSA-USPIO enhanced MRI, especially T2*-weighted sequences, with a signal strength peaking at 96 h. The group given atorvastatin showed few DMSA-USPIO particles and had lower levels of serum indicators. MMP-9 and sCD40L levels in group B were significantly higher than in the other 2 groups (P <0.05).
Conclusion: After successfully establishing a VP model in rabbits, DMSA-USPIO was used to enhance MRI for clear identification of plaque inflammation and rupture. Rupture plaques were detectable in this way probably due to an activating inflammatory process. Atorvastatin reduced the inflammatory response and stabilizing VP possibly by decreasing MMP-9 and sCD40L levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Detection of Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaques in Experimental Atherosclerosis with the USPIO-Enhanced MRI.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Nov;73(2):331-337. doi: 10.1007/s12013-015-0591-y. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 27352319
-
[Predictors of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques induced by cholesterol and balloon injury in rabbits].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;39(4):343-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2011.04.013. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21624311 Chinese.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stabilize Atherosclerotic Vulnerable Plaque by Anti-Inflammatory Properties.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0136026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136026. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26288013 Free PMC article.
-
[Iron-oxide-enhanced MR imaging of inflammatory atherosclerotic lesions: overview of experimental and initial clinical results].Rofo. 2003 Apr;175(4):469-76. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38434. Rofo. 2003. PMID: 12677500 Review. German.
-
Histological validation of iron-oxide and gadolinium based MRI contrast agents in experimental atherosclerosis: the do's and don't's.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Dec;225(2):274-80. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.07.028. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22882907 Review.
Cited by
-
Desipramine enhances the stability of atherosclerotic plaque in rabbits monitored with molecular imaging.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 30;18(3):e0283612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283612. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36996033 Free PMC article.
-
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;11(9):2337. doi: 10.3390/nano11092337. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34578651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II-accelerated vulnerability of carotid plaque in a cholesterol-fed rabbit model-assessed with magnetic resonance imaging comparing to histopathology.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017 Mar;24(3):495-503. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28386172 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Albumin ECM Accumulation and Inflammation as Novel In Vivo Diagnostic Targets for Multi-Target MR Imaging.Biology (Basel). 2021 Sep 27;10(10):964. doi: 10.3390/biology10100964. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681063 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Imaging of Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaques in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 9;17(9):1511. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091511. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27618031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

