The HIV Care Cascade Before, During, and After Incarceration: A Systematic Review and Data Synthesis
- PMID: 25973818
- PMCID: PMC4463395
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302635
The HIV Care Cascade Before, During, and After Incarceration: A Systematic Review and Data Synthesis
Erratum in
-
ERRATUM.Am J Public Health. 2018 Mar;108(3):e18. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302635e. Am J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29412727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
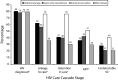
We conducted a systematic literature review of the data on HIV testing, engagement in care, and treatment in incarcerated persons, and estimated the care cascade in this group. We identified 2706 titles in MEDLINE, EBSCO, and Cochrane Library databases for studies indexed to January 13, 2015, and included 92 for analysis. We summarized HIV testing results by type (blinded, opt-out, voluntary); reviewed studies on HIV care engagement, treatment, and virological suppression; and synthesized these results into an HIV care cascade before, during, and after incarceration. The HIV care cascade following diagnosis increased during incarceration and declined substantially after release, often to levels lower than before incarceration. Incarceration provides an opportunity to address HIV care in hard-to-reach individuals, though new interventions are needed to improve postrelease care continuity.
Figures

References
-
- National HIV/AIDS Strategy for the United States. Washington, DC: The White House; 2010.
-
- Obama B. Washington, DC: The White House, Office of the Press Secretary; 2013. HIV care continuum initiative.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital signs: HIV prevention through care and treatment—United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60(47):1618–1623. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data—United States and 6 dependent areas—2011. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2013;18(5)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

