Cullin 3 Recognition Is Not a Universal Property among KCTD Proteins
- PMID: 25974686
- PMCID: PMC4431850
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126808
Cullin 3 Recognition Is Not a Universal Property among KCTD Proteins
Abstract
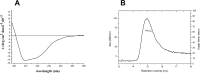
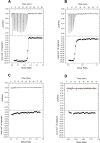
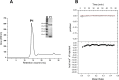
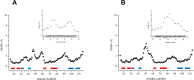
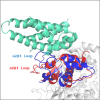
Cullin 3 (Cul3) recognition by BTB domains is a key process in protein ubiquitination. Among Cul3 binders, a great attention is currently devoted to KCTD proteins, which are implicated in fundamental biological processes. On the basis of the high similarity of BTB domains of these proteins, it has been suggested that the ability to bind Cul3 could be a general property among all KCTDs. In order to gain new insights into KCTD functionality, we here evaluated and/or quantified the binding of Cul3 to the BTB of KCTD proteins, which are known to be involved either in cullin-independent (KCTD12 and KCTD15) or in cullin-mediated (KCTD6 and KCTD11) activities. Our data indicate that KCTD6(BTB) and KCTD11(BTB) bind Cul3 with high affinity forming stable complexes with 4:4 stoichiometries. Conversely, KCTD12(BTB) and KCTD15(BTB) do not interact with Cul3, despite the high level of sequence identity with the BTB domains of cullin binding KCTDs. Intriguingly, comparative sequence analyses indicate that the capability of KCTD proteins to recognize Cul3 has been lost more than once in distinct events along the evolution. Present findings also provide interesting clues on the structural determinants of Cul3-KCTD recognition. Indeed, the characterization of a chimeric variant of KCTD11 demonstrates that the swapping of α2β3 loop between KCTD11(BTB) and KCTD12(BTB) is sufficient to abolish the ability of KCTD11(BTB) to bind Cul3. Finally, present findings, along with previous literature data, provide a virtually complete coverage of Cul3 binding ability of the members of the entire KCTD family.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Skoblov M, Marakhonov A, Marakasova E, Guskova A, Chandhoke V, Birerdinc A, et al. (2013) Protein partners of KCTD proteins provide insights about their functional roles in cell differentiation and vertebrate development. BioEssays: news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology 35: 586–596. 10.1002/bies.201300002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Birerdinc A, Nohelty E, Marakhonov A, Manyam G, Panov I, Coon S, et al. (2010) Pro-apoptotic and antiproliferative activity of human KCNRG, a putative tumor suppressor in 13q14 region. Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 31: 33–45. 10.1007/s13277-009-0005-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

