Emerging Targets for Therapeutic Development in Diabetes and Its Complications: The RAGE Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 25974754
- PMCID: PMC4621004
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.148
Emerging Targets for Therapeutic Development in Diabetes and Its Complications: The RAGE Signaling Pathway
Abstract
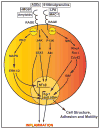
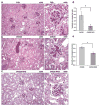
Types 1 and 2 diabetes are on the rise worldwide. Although the treatment of hyperglycemia has benefited from recent advances, aggressive efforts to maintain euglycemia may be fraught with risk, especially in older subjects or in subjects vulnerable to hypoglycemic unawareness. Hence, strategies to prevent and treat the complications of hyperglycemia are essential. In this review we summarize recent updates on the biology of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) in the pathogenesis of both micro- and macrovascular complications of diabetes, insights from the study of mouse models of obesity and diabetic complications, and from associative studies in human subjects. The study of the mechanisms and consequences of the interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with the formin, mDia1, in RAGE signal transduction, will be discussed. Lastly, we review the "state-of-the-art" on RAGE-directed therapeutics. Tackling RAGE/mDia1 may identify a novel class of therapeutics preventing diabetes and its complications.
© 2015 American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
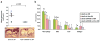
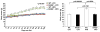

References
-
- WHO. [Accessed 9 February 2015];Obesity and Overweight. 2015 < http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/>.
-
- CDC. [Accessed 9 February 2015];Adult Obesity Facts. 2014 < http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html>.
-
- CDC. National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2014 < http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/statsreport14/national-diabetes-report-...>.
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Med. 1998;15:539–553. - PubMed
-
- Gaens KH, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG. Advanced glycation endproducts and its receptor for advanced glycation endproducts in obesity. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2013;24:4–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

