Spontaneous rupture of a congenital diaphragmatic eventration in an infant
- PMID: 25976306
- PMCID: PMC4434382
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-208634
Spontaneous rupture of a congenital diaphragmatic eventration in an infant
Abstract
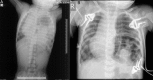
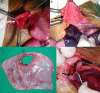
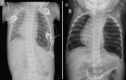
Rupture of the diaphragm may be traumatic or spontaneous. A spontaneous rupture occurring in a congenital eventration of the diaphragm is extremely rare. Only one such case has been reported previously. We report a case of a 5-month-old male infant who presented with acute life-threatening respiratory distress secondary to spontaneous rupture of a congenital diaphragmatic eventration.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Heuckmann LKP, Schleef J, Uekotter J. Diaphragmatic rupture in pertussis. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 1996;144:259–62.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
