Neurodegeneration. C9ORF72 repeat expansions in mice cause TDP-43 pathology, neuronal loss, and behavioral deficits
- PMID: 25977373
- PMCID: PMC4692360
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaa9344
Neurodegeneration. C9ORF72 repeat expansions in mice cause TDP-43 pathology, neuronal loss, and behavioral deficits
Abstract
The major genetic cause of frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a G4C2 repeat expansion in C9ORF72. Efforts to combat neurodegeneration associated with "c9FTD/ALS" are hindered by a lack of animal models recapitulating disease features. We developed a mouse model to mimic both neuropathological and clinical c9FTD/ALS phenotypes. We expressed (G4C2)66 throughout the murine central nervous system by means of somatic brain transgenesis mediated by adeno-associated virus. Brains of 6-month-old mice contained nuclear RNA foci, inclusions of poly(Gly-Pro), poly(Gly-Ala), and poly(Gly-Arg) dipeptide repeat proteins, as well as TDP-43 pathology. These mouse brains also exhibited cortical neuron and cerebellar Purkinje cell loss, astrogliosis, and decreased weight. (G4C2)66 mice also developed behavioral abnormalities similar to clinical symptoms of c9FTD/ALS patients, including hyperactivity, anxiety, antisocial behavior, and motor deficits.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
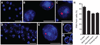

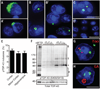
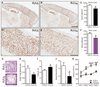
Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Expanding neurodegeneration modelling.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Jul;16(7):376. doi: 10.1038/nrn3982. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26036208 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01NS077402/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS089979/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS089979/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS079807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES20395/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063964/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS063964/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS088689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS079807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS084528/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020395/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS077402/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS084528/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

