Differential mucin expression by respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus infection in human epithelial cells
- PMID: 25977598
- PMCID: PMC4421075
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/347292
Differential mucin expression by respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus infection in human epithelial cells
Abstract
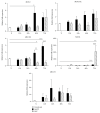
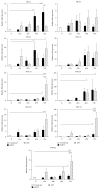
Mucins (MUC) constitute an important component of the inflammatory and innate immune response. However, the expression of these molecules by respiratory viral infections is still largely unknown. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) are two close-related paramyxoviruses that can cause severe low respiratory tract disease in infants and young children worldwide. Currently, there is not vaccine available for neither virus. In this work, we explored the differential expression of MUC by RSV and hMPV in human epithelial cells. Our data indicate that the MUC expression by RSV and hMPV differs significantly, as we observed a stronger induction of MUC8, MUC15, MUC20, MUC21, and MUC22 by RSV infection while the expression of MUC1, MUC2, and MUC5B was dominated by the infection with hMPV. These results may contribute to the different immune response induced by these two respiratory viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Rose M. C. Mucins: structure, function, and role in pulmonary diseases. American Journal of Physiology—Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 1992;263(4):L413–L429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

