Genomes and phenomes of a population of outbred rats and its progenitors
- PMID: 25977769
- PMCID: PMC4381735
- DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2014.11
Genomes and phenomes of a population of outbred rats and its progenitors
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Genomes and phenomes of a population of outbred rats and its progenitors.Sci Data. 2014 Jul 8;1:140016. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2014.16. eCollection 2014. Sci Data. 2014. PMID: 25982460 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Finding genetic variants that contribute to phenotypic variation is one of the main challenges of modern genetics. We used an outbred population of rats (Heterogeneous Stock, HS) in a combined sequence-based and genetic mapping analysis to identify sequence variants and genes contributing to complex traits of biomedical relevance. Here we describe the sequences of the eight inbred progenitors of the HS and the variants that segregate between them. We report the genotyping of 1,407 HS rats, and the collection from 2,006 rats of 195 phenotypic measures that are relevant to models of anxiety, type 2 diabetes, hypertension and osteoporosis. We make available haplotype dosages for the 1,407 genotyped rats, since genetic mapping in the HS is best carried out by reconstructing each HS chromosome as a mosaic of the progenitor genomes. Finally, we have deposited an R object that makes it easy to incorporate our sequence data into any genetic study of HS rats. Our genetic data are available for both Rnor3.4 and Rnor5.0 rat assemblies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
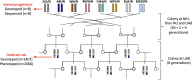

Comment in
-
Ctrl alt share.Sci Data. 2015 Feb 17;2:150004. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2015.4. eCollection 2015. Sci Data. 2015. PMID: 25977811 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Data Citations
-
- The Rat Genome Sequencing and Mapping Consortium 2014. ArrayExpress. E-MTAB-2332
-
- The Rat Genome Sequencing and Mapping Consortium 2014. Figshare. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.943485 - DOI
References
-
- Hansen C., Spuhler K. Development of the National Institutes of Health genetically heterogeneous rat stock. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 8, 477–479 (1984). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

