Human olfactory receptor responses to odorants
- PMID: 25977809
- PMCID: PMC4412152
- DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2015.2
Human olfactory receptor responses to odorants
Abstract
Although the human olfactory system is capable of discriminating a vast number of odors, we do not currently understand what chemical features are encoded by olfactory receptors. In large part this is due to a paucity of data in a search space covering the interactions of hundreds of receptors with billions of odorous molecules. Of the approximately 400 intact human odorant receptors, only 10% have a published ligand. Here we used a heterologous luciferase assay to screen 73 odorants against a clone library of 511 human olfactory receptors. This dataset will allow other researchers to interrogate the combinatorial nature of olfactory coding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
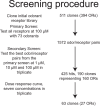




Dataset use reported in
- doi: 10.1038/nn.3598
References
Data Citations
-
- Mainland J. D., Yun R. L., Zhou T., Liu W. L. L., Matsunami H. 2014. Figshare. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.979135 - DOI
References
-
- Araneda R. C., Kini A. D. & Firestein S. The molecular receptive range of an odorant receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1248–1255 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Malnic B., Hirono J., Sato T. & Buck L. B. Combinatorial receptor codes for odors. Cell 96, 713–723 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Saito H., Kubota M., Roberts R., Chi Q. & Matsunami H. RTP family members induce functional expression of mammalian odorant receptors. Cell 119, 679–691 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

