Acute adult-onset still's disease presenting as pulmonary hemorrhage, urticaria, angioedema and leukemoid reaction: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 25977887
- PMCID: PMC4414853
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-0924-8
Acute adult-onset still's disease presenting as pulmonary hemorrhage, urticaria, angioedema and leukemoid reaction: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Adult-onset Still's disease is a rare systemic inflammatory disorder of unknown aetiology characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash however, the multiorgan involvement can be present.
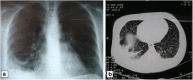
Case description: A 40-year-old woman previously healthy was referred to our hospital with 7 days of high fever and generalized arthralgia, The physical exam revealed angioneurotic edema detected on soles, palms and tongue and widespread red, urticated plaques in a symmetrical distribution affecting the arms, dorsal hands, upper and lower chest and back. Followed 5 days later by fever, the patient presented dyspnea, cough and hypoxemia, the imaging studies showed unilateral consolidation and pleural effusion. The bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage and skin biopsy were consistent with neutrophilic urticarial. The hematological disorders, infections and other autoimmune diseases were excluded.
Discussion and evaluation: The diagnosis of adult-onset Still's disease can be very difficult. There are no specific tests and reliance is usually placed on a symptom complex and the well described typical rash seen in most patients. In recent years, however, other cutaneous manifestations of Adult-onset Still's disease have been reported but these are not so well known.
Conclusions: The evidence of rare manifestations is growing and the early clinical presentation of Adult-onset Still's is extremely variable, making diagnosis difficult. For this reason, data on early clinical presentation of the disease are of interest. We reported the first case of acute Adult-onset Still's disease with the association of pulmonary hemorrhage, urticaria and angioedema including a rare systemic manifestation as leukemoid reaction.
Keywords: Adult-onset still’s disease; Angioedema; Leukemoid reaction; Pulmonary hemorrhage; Urticaria.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cutaneous manifestations of adult-onset Still's disease: a case report and review of literature.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 May;35(5):1377-82. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2614-2. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 24737284 Review.
-
Atypical Skin Rash in a Patient with Adult-Onset Still's Disease: A Case Report.Oman Med J. 2013 Jul;28(4):e052. doi: 10.5001/omj.2013.86. Oman Med J. 2013. PMID: 31435474 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Adult-Onset Still's Disease Presenting with Urticated Plaques and Acute Myopericarditis.Indian J Dermatol. 2013 Sep;58(5):405. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.117316. Indian J Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 24082197 Free PMC article.
-
Adult-onset Still's disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation and hemophagocytic syndrome: a case report.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Dec 22;7:940. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-940. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25532568 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18 as a diagnostic marker of adult-onset Still's disease in older patients: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Jul 10;12(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1735-7. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29986752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A case of a 22-month-old boy with necrotizing pneumonia presenting with leukaemoid reaction misdiagnosed as leukaemia: a case report and review of the literature.Malawi Med J. 2019 Sep;31(3):223-226. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v31i3.10. Malawi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31839893 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab for uncontrollable systemic inflammatory response syndrome complicating adult-onset Still disease: Case report and review of literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(29):e7596. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007596. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28723802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inadvertent Skipping of Steroids in Septic Shock Leads to a Diagnosis of Adult Onset Still's Disease.Cureus. 2017 Jan 14;9(1):e978. doi: 10.7759/cureus.978. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 28191382 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

