Quantitative Assessment of the Influence of Rhizoma Zingiberis on the Level of Aconitine in Rat Gut Sacs and Qualitative Analysis of the Major Influencing Components of Rhizoma Zingiberis on Aconitine Using UPLC/MS
- PMID: 25978042
- PMCID: PMC4433269
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124110
Quantitative Assessment of the Influence of Rhizoma Zingiberis on the Level of Aconitine in Rat Gut Sacs and Qualitative Analysis of the Major Influencing Components of Rhizoma Zingiberis on Aconitine Using UPLC/MS
Abstract
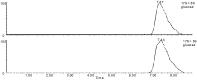
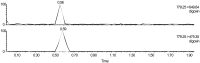
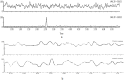
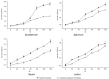
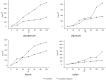
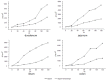
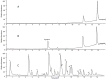
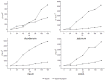
This study attempted to clarify the material basis for the detoxification of Rhizoma Zingiberis (RZ) on aconitine, an analgesic drug, by quantitatively assessing the influence of RZ on the in vitro intestinal concentration of aconitine using an everted gut sac model and by qualitatively identifying the components in the RZ extract. To quantify aconitine in rat everted gut sacs, both an accurate processing method and a sensitive detection method were required. We developed a three-step sample processing method to protect the components from decomposition and applied ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC/TQMS) to quantify aconitine, glucose and digoxin. In addition, ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap mass spectrometry (UPLC/ITMS) was applied to detect the potential antidotal components in the RZ extract. Finally, the RZ extract reduced the level of aconitine in everted gut sacs, and eleven gingerols were successfully identified, which could be considered potential antidotal components for aconitine. This study demonstrated the application of two UPLC/MS methods for analyzing the material basis for the reciprocity between Chinese medicine components in everted gut sacs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a highly sensitive UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, and five of their metabolites in rat blood and its application to a pharmacokinetics study of aconitine, mesaconitine, and hypaconitine.Xenobiotica. 2012 Jun;42(6):518-25. doi: 10.3109/00498254.2011.641608. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Xenobiotica. 2012. PMID: 22188409
-
Analysis and pharmacokinetic study of curdione in Rhizoma Curcumae by UPLC/QTOF/MS.Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Jun;28(6):782-7. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3118. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014. PMID: 24861744
-
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Saponins in Panacis Japonici Rhizoma Using Ultra-Fast Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Triple Quadrupole-Time of Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Ultra-Fast Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Triple Quadrupole-Linear Ion Trap Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019;67(8):839-848. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c19-00255. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 31366833
-
Metabonomic study on 'Kidney-Yang Deficiency syndrome' and intervention effects of Rhizoma Drynariae extracts in rats using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry.Talanta. 2011 Jan 15;83(3):700-8. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2010.09.026. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Talanta. 2011. PMID: 21147309
-
Quality assessment of crude and processed ginger by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics.J Sep Sci. 2015 Sep;38(17):2945-52. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201500294. J Sep Sci. 2015. PMID: 26174663
Cited by
-
A critical courier role of volatile oils from Dalbergia odorifera for cardiac protection in vivo by QiShenYiQi.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7353. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07659-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779167 Free PMC article.
-
Acupoint herbal plaster for patients with primary dysmenorrhea: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Jul 3;19(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2682-8. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29970155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaheen F, Ahmad M, Khan MTH, Jalil S, Ejaz A, Sultankhodjaev MN, et al. Alkaloids of Aconitum laeve and their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibition activities. Phytochemistry. 2005; 66:935–940. - PubMed
-
- Liou SS, Liu IM, Lai MC, Cheng JT. Comparison of the antinociceptive action of crude Fuzei, the root of Aconitum, and its processed products. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005; 99: 379–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

