Medicinal plants recommended by the world health organization: DNA barcode identification associated with chemical analyses guarantees their quality
- PMID: 25978064
- PMCID: PMC4433216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127866
Medicinal plants recommended by the world health organization: DNA barcode identification associated with chemical analyses guarantees their quality
Abstract
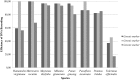
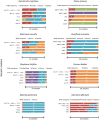
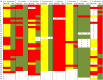
Medicinal plants are used throughout the world, and the regulations defining their proper use, such as identification of the correct species and verification of the presence, purity and concentration of the required chemical compounds, are widely recognized. Herbal medicines are made from vegetal drugs, the processed products of medicinal species. These processed materials present a number of challenges in terms of botanical identification, and according to the World Health Organization (WHO), the use of incorrect species is a threat to consumer safety. The samples used in this study consisted of the dried leaves, flowers and roots of 257 samples from 8 distinct species approved by the WHO for the production of medicinal herbs and sold in Brazilian markets. Identification of the samples in this study using DNA barcoding (matK, rbcL and ITS2 regions) revealed that the level of substitutions may be as high as 71%. Using qualitative and quantitative chemical analyses, this study identified situations in which the correct species was being sold, but the chemical compounds were not present. Even more troubling, some samples identified as substitutions using DNA barcoding contained the chemical compounds from the correct species at the minimum required concentration. This last situation may lead to the use of unknown species or species whose safety for human consumption remains unknown. This study concludes that DNA barcoding should be used in a complementary manner for species identification with chemical analyses to detect and quantify the required chemical compounds, thus improving the quality of this class of medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrating DNA Barcoding Within an Orthogonal Approach for Herbal Product Authentication: A Narrative Review.Phytochem Anal. 2025 Jan;36(1):7-29. doi: 10.1002/pca.3466. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Phytochem Anal. 2025. PMID: 39532481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of processed Chinese medicinal materials using DNA mini-barcoding.Chin J Nat Med. 2017 Jul;15(7):481-486. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(17)30073-0. Chin J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28807221
-
DNA barcoding of medicinal orchids in Asia.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 8;11(1):23651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03025-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34880330 Free PMC article.
-
Creation of reference DNA barcode library and authentication of medicinal plant raw drugs used in Ayurvedic medicine.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 18;16 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1086-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27454470 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the use of DNA barcodes in the identification and classification of medicinal plants.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Jan 15;208:111691. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111691. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33396023 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis of fluorescent silver nanoparticles from Leea coccinea leaves and their antibacterial potentialities against Xanthomonas phaseoli pv phaseoli.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021 Jan 4;8(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40643-020-00354-2. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021. PMID: 38650222 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating DNA Barcoding Within an Orthogonal Approach for Herbal Product Authentication: A Narrative Review.Phytochem Anal. 2025 Jan;36(1):7-29. doi: 10.1002/pca.3466. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Phytochem Anal. 2025. PMID: 39532481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of two herbal formulas for gastrointestinal function and gut microbiota modulation in rats with loperamide-induced dyspepsia.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 25;15(1):31186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15574-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40854940 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Chloroplast Genomes among Species of Unisexual and Bisexual Clades of the Monocot Family Araceae.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jun 11;9(6):737. doi: 10.3390/plants9060737. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545339 Free PMC article.
-
Pitfalls and promises of raw drug identification techniques in the ayurvedic industry: an overview.3 Biotech. 2020 Nov;10(11):497. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02482-0. Epub 2020 Oct 30. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 33150123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO (World Health Organization) (2011) The World Traditional Medicines Situation, in Traditional medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges. Geneva 3:1–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

