Molecular-interaction and signaling profiles of AM3677, a novel covalent agonist selective for the cannabinoid 1 receptor
- PMID: 25978068
- PMCID: PMC4804703
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00090
Molecular-interaction and signaling profiles of AM3677, a novel covalent agonist selective for the cannabinoid 1 receptor
Abstract
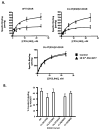
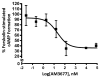
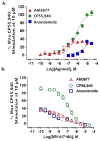
The cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB1R) is one of the most abundant G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the central nervous system. CB1R involvement in multiple physiological processes, especially neurotransmitter release and synaptic function, has made this GPCR a prime drug discovery target, and pharmacological CB1R activation has been demonstrated to be a tenable therapeutic modality. Accordingly, the design and profiling of novel, drug-like CB1R modulators to inform the receptor's ligand-interaction landscape and molecular pharmacology constitute a prime contemporary research focus. For this purpose, we report utilization of AM3677, a designer endocannabinoid (anandamide) analogue derivatized with a reactive electrophilic isothiocyanate functionality, as a covalent, CB1R-selective chemical probe. The data demonstrate that reaction of AM3677 with a cysteine residue in transmembrane helix 6 of human CB1R (hCB1R), C6.47(355), is a key feature of AM3677's ligand-binding motif. Pharmacologically, AM3677 acts as a high-affinity, low-efficacy CB1R agonist that inhibits forskolin-stimulated cellular cAMP formation and stimulates CB1R coupling to G protein. AM3677 also induces CB1R endocytosis and irreversible receptor internalization. Computational docking suggests the importance of discrete hydrogen bonding and aromatic interactions as determinants of AM3677's topology within the ligand-binding pocket of active-state hCB1R. These results constitute the initial identification and characterization of a potent, high-affinity, hCB1R-selective covalent agonist with utility as a pharmacologically active, orthosteric-site probe for providing insight into structure-function correlates of ligand-induced CB1R activation and the molecular features of that activation by the native ligand, anandamide.
Keywords: 7-transmembrane receptor; Amino acid; G protein-coupled receptor; binding domain; central nervous system; chemical probe; cysteine; homology modeling; isothiocyanate; ligand-binding motif; receptor activation; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
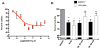

References
-
- Di Marzo V. The endocannabinoid system: its general strategy of action, tools for its pharmacological manipulation and potential therapeutic exploration. Pharmacol Res. 2009;60:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Mechoulam R, Parker LA. The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu Rev Pscyhol. 2013;64:21–47. - PubMed
-
- Ohno-Shosaku T, Kano M. Endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;29:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Ashton CH, Moore PB. Endocannabinoid system dysfunction in mood and related disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2011;124:250–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

