Small-molecule modulators of the constitutive androstane receptor
- PMID: 25979168
- PMCID: PMC4469626
- DOI: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1043887
Small-molecule modulators of the constitutive androstane receptor
Abstract
Introduction: The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) induces drug-metabolizing enzymes for xenobiotic metabolism.
Areas covered: This review covers recent advances in elucidating the biological functions of CAR and its modulation by a growing number of agonists and inhibitors.
Expert opinion: Extrapolation of animal CAR function to that of humans should be carefully scrutinized, particularly when rodents are used in evaluating the metabolic profile and carcinogenic properties of clinical drugs and environmental chemicals. Continuous efforts are needed to discover novel CAR inhibitors, with extensive understanding of their inhibitory mechanism, species selectivity, and discriminating power against other xenobiotic sensors.
Keywords: constitutive androstane receptor; drug–drug interactions; small-molecule; xenobiotic metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
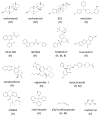

References
-
- Wang H, Faucette S, Sueyoshi T, et al. A novel distal enhancer module regulated by pregnane X receptor/constitutive androstane receptor is essential for the maximal induction of CYP2B6 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14146–52. - PubMed
-
- Min G, Kim H, Bae Y, et al. Inhibitory cross-talk between estrogen receptor (ER) and constitutively activated androstane receptor (CAR). CAR inhibits ER-mediated signaling pathway by squelching p160 coactivators. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:34626–33. - PubMed
-
- Choi HS, Chung M, Tzameli I, et al. Differential transactivation by two isoforms of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor CAR. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:23565–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
