Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions
- PMID: 25979354
- PMCID: PMC4433489
- DOI: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066
Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions
Abstract
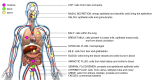
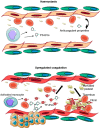
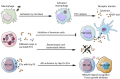
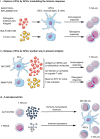
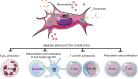
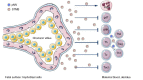
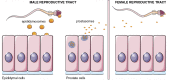
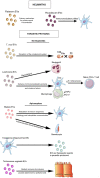
In the past decade, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been recognized as potent vehicles of intercellular communication, both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This is due to their capacity to transfer proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, thereby influencing various physiological and pathological functions of both recipient and parent cells. While intensive investigation has targeted the role of EVs in different pathological processes, for example, in cancer and autoimmune diseases, the EV-mediated maintenance of homeostasis and the regulation of physiological functions have remained less explored. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of the physiological roles of EVs, which has been written by crowd-sourcing, drawing on the unique EV expertise of academia-based scientists, clinicians and industry based in 27 European countries, the United States and Australia. This review is intended to be of relevance to both researchers already working on EV biology and to newcomers who will encounter this universal cell biological system. Therefore, here we address the molecular contents and functions of EVs in various tissues and body fluids from cell systems to organs. We also review the physiological mechanisms of EVs in bacteria, lower eukaryotes and plants to highlight the functional uniformity of this emerging communication system.
Keywords: eukaryote; exosome; extracellular vesicle; microparticle; microvesicle; physiology; prokaryote.
Figures


References
-
- Waters CM, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:319–46. - PubMed
-
- Chargaff E, West R. The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J Biol Chem. 1946;166:189–97. - PubMed
-
- Wolf P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967;13:269–88. - PubMed
-
- De Broe M, Wieme R, Roels F. Letter: membrane fragments with koinozymic properties released from villous adenoma of the rectum. Lancet. 1975;2:1214–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

