Reduced-fat foods: the complex science of developing diet-based strategies for tackling overweight and obesity
- PMID: 25979507
- PMCID: PMC4424772
- DOI: 10.3945/an.114.006999
Reduced-fat foods: the complex science of developing diet-based strategies for tackling overweight and obesity
Abstract
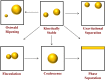
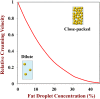
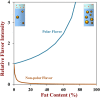
Fat plays multiple roles in determining the desirable physicochemical properties, sensory attributes, nutritional profile, and biologic response of food products. Overconsumption of fats is linked to chronic diseases, such as obesity, coronary heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. There is therefore a need to develop reduced-fat products with physicochemical properties and sensory profiles that match those of their full-fat counterparts. In addition, foods may be redesigned to increase the feelings of satiety and satiation, and thereby reduce overall food intake. The successful design of these types of functional foods requires a good understanding of the numerous roles that fat plays in determining food attributes and the development of effective strategies to replace these attributes. This article provides an overview of the current understanding of the influence of fat on the physicochemical and physiologic attributes of emulsion-based food products and highlights approaches to create high-quality foods with reduced-fat contents.
Keywords: emulsions; food design; food matrix effects; functional foods; obesity; overweight; reduced-fat; satiety.
© 2015 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosure: DJ McClements, no conflicts of interest.
Figures





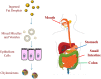




Similar articles
-
Reduced Fat Food Emulsions: Physicochemical, Sensory, and Biological Aspects.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016;56(4):650-85. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2013.792236. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25748819 Review.
-
Differing effects of high-fat or high-carbohydrate meals on food hedonics in overweight and obese individuals.Br J Nutr. 2016 May 28;115(10):1875-84. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516000775. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27001260 Clinical Trial.
-
Fat as a risk factor for overconsumption: satiation, satiety, and patterns of eating.J Am Diet Assoc. 1997 Jul;97(7 Suppl):S63-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8223(97)00733-5. J Am Diet Assoc. 1997. PMID: 9216571 Review.
-
The role of energy density in the overconsumption of fat.J Nutr. 2000 Feb;130(2S Suppl):268S-271S. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.2.268S. J Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10721885 Review.
-
The role of dietary fat in body fatness: evidence from a preliminary meta-analysis of ad libitum low-fat dietary intervention studies.Br J Nutr. 2000 Mar;83 Suppl 1:S25-32. doi: 10.1017/s0007114500000921. Br J Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10889789
Cited by
-
Challenges of utilizing healthy fats in foods.Adv Nutr. 2015 May 15;6(3):309S-17S. doi: 10.3945/an.114.006965. Print 2015 May. Adv Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25979504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Use of Cold-Pressed Pumpkin Seed Oil By-Products in a Low-Fat Salad Dressing: The Effect on Rheological, Microstructural, Recoverable Properties, and Emulsion and Oxidative Stability.Foods. 2021 Nov 10;10(11):2759. doi: 10.3390/foods10112759. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34829043 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous enzymatic saccharification and comminution for the valorization of lignocellulosic biomass toward natural products.BMC Biotechnol. 2018 Dec 12;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12896-018-0487-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30541521 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Cellulose Ethers on the Physico-Chemical Properties, Structure and Lipid Digestibility of Animal Fat Emulsions Stabilized by Soy Protein.Foods. 2022 Mar 2;11(5):738. doi: 10.3390/foods11050738. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35267370 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and Factors Associated with Obesity Prevalence in Rural Australian Adults-Comparative Analysis of the Crossroads Studies in Victoria over 15 Years.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 28;14(21):4557. doi: 10.3390/nu14214557. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brawer R, Brisbon N, Plumb J. Obesity and cancer. Prim Care 2009;36(3):509. - PubMed
-
- Schrauwen P, Saris WHM. Dietary fat and obesity. In: Williams C, Buttriss J, editors. Improving the fat content of foods. Bocan Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2006. p. 141–61.
-
- Swinburn BA, Caterson I, Seidell JC, James WPT. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity. Public Health Nutr 2004;7(1A):123–46. - PubMed
-
- Friberg S, Larsson K, Sjoblom J. Food emulsions. 4th ed. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
-
- McClements DJ. Food emulsions: principles, practices, and techniques. 2nd ed. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

