Do Genetic Susceptibility Variants Associate with Disease Severity in Early Active Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- PMID: 25979711
- PMCID: PMC6714044
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.141211
Do Genetic Susceptibility Variants Associate with Disease Severity in Early Active Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Abstract
Objective: Genetic variants affect both the development and severity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recent studies have expanded the number of RA susceptibility variants. We tested the hypothesis that these associated with disease severity in a clinical trial cohort of patients with early, active RA.
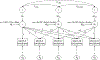
Methods: We evaluated 524 patients with RA enrolled in the Combination Anti-Rheumatic Drugs in Early RA (CARDERA) trials. We tested validated susceptibility variants - 69 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), 15 HLA-DRB1 alleles, and amino acid polymorphisms in 6 HLA molecule positions - for their associations with progression in Larsen scoring, 28-joint Disease Activity Scores, and Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) scores over 2 years using linear mixed-effects and latent growth curve models.
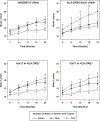
Results: HLA variants were associated with joint destruction. The *04:01 SNP (rs660895, p = 0.0003), *04:01 allele (p = 0.0002), and HLA-DRβ1 amino acids histidine at position 13 (p = 0.0005) and valine at position 11 (p = 0.0012) significantly associated with radiological progression. This association was only significant in anticitrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive patients, suggesting that while their effects were not mediated by ACPA, they only predicted joint damage in ACPA-positive RA. Non-HLA variants did not associate with radiograph damage (assessed individually and cumulatively as a weighted genetic risk score). Two SNP - rs11889341 (STAT4, p = 0.0001) and rs653178 (SH2B3-PTPN11, p = 0.0004) - associated with HAQ scores over 6-24 months.
Conclusion: HLA susceptibility variants play an important role in determining radiological progression in early, active ACPA-positive RA. Genome-wide and HLA-wide analyses across large populations are required to better characterize the genetic architecture of radiological progression in RA.
Keywords: GENETICS; HLA ANTIGENS; OUTCOME MEASURES; RADIOGRAPHY; RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS.
Figures
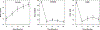

Similar articles
-
HLA-DRB1 Amino Acid Positions 11/13, 71, and 74 Are Associated With Inflammation Level, Disease Activity, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Score in Patients With Inflammatory Polyarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;68(11):2618-2628. doi: 10.1002/art.39780. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27274008 Free PMC article.
-
Brief Report: Main Contribution of DRB1*04:05 Among the Shared Epitope Alleles and Involvement of DRB1 Amino Acid Position 57 in Association With Joint Destruction in Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jul;67(7):1744-50. doi: 10.1002/art.39105. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25777156
-
Association of HLA-DRB1 haplotypes with rheumatoid arthritis severity, mortality, and treatment response.JAMA. 2015 Apr 28;313(16):1645-56. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.3435. JAMA. 2015. PMID: 25919528 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of human leukocyte antigen-DRB1 on the susceptibility and severity of rheumatoid arthritis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jun;31(6):355-60. doi: 10.1053/sarh.2002.32552. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12077707 Review.
-
[Is rheumatoid arthritis without anti-citrullinated peptide antibody a genetically distinct subset?].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2009 Dec;32(6):484-91. doi: 10.2177/jsci.32.484. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2009. PMID: 20046016 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Association between PYTPN22 rs2476601, VEGF rs833070, TNFAIP3 rs6920220 Polymorphisms and Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Undifferentiated Arthritis Patients: A Pilot Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 13;59(10):1824. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101824. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893542 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DRB1 Amino Acid Positions 11/13, 71, and 74 Are Associated With Inflammation Level, Disease Activity, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Score in Patients With Inflammatory Polyarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;68(11):2618-2628. doi: 10.1002/art.39780. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27274008 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility, severity, and treatment response.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jun;39(4):395-408. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0630-4. Epub 2017 May 29. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28555384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic associations with radiological damage in rheumatoid arthritis: Meta-analysis of seven genome-wide association studies of 2,775 cases.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 9;14(10):e0223246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223246. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31596875 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic puzzle of rheumatoid arthritis: Causes, progression, and treatment.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jul 21;43:102148. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102148. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40734997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Knevel R, Gröndal G, Huizinga TW, Visser AW, Jónsson H, Víkingsson A, et al. Genetic predisposition of the severity of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:707–9. - PubMed
-
- van Steenbergen HW, Tsonaka R, Huizinga TW, le Cessie S, van der Helm-van Mil AM. Predicting the severity of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis; the contribution of genetic factors. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:876–82. - PubMed
-
- Knevel R, de Rooy DP, Gregersen PK, Lindqvist E, Wilson AG, Grondal G, et al. Studying associations between variants in TRAF1-C5 and TNFAIP3-OLIG3 and the progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis in multiple cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1753–5. - PubMed
-
- Marinou I, Maxwell JR, Wilson AG. Genetic influences modulating the radiological severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:476–82. - PubMed
-
- de Rooy DP, Zhernakova A, Tsonaka R, Willemze A, Kurreeman BA, Trynka G, et al. A genetic variant in the region of MMP-9 is associated with serum levels and progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1163–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
