Adult height, coronary heart disease and stroke: a multi-locus Mendelian randomization meta-analysis
- PMID: 25979724
- PMCID: PMC5841831
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyv074
Adult height, coronary heart disease and stroke: a multi-locus Mendelian randomization meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: We investigated causal effect of completed growth, measured by adult height, on coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke and cardiovascular traits, using instrumental variable (IV) Mendelian randomization meta-analysis.
Methods: We developed an allele score based on 69 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with adult height, identified by the IBCCardioChip, and used it for IV analysis against cardiovascular risk factors and events in 21 studies and 60 028 participants. IV analysis on CHD was supplemented by summary data from 180 height-SNPs from the GIANT consortium and their corresponding CHD estimates derived from CARDIoGRAMplusC4D.
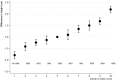
Results: IV estimates from IBCCardioChip and GIANT-CARDIoGRAMplusC4D showed that a 6.5-cm increase in height reduced the odds of CHD by 10% [odds ratios 0.90; 95% confidence intervals (CIs): 0.78 to 1.03 and 0.85 to 0.95, respectively],which agrees with the estimate from the Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration (hazard ratio 0.93; 95% CI: 0.91 to 0.94). IV analysis revealed no association with stroke (odds ratio 0.97; 95% CI: 0.79 to 1.19). IV analysis showed that a 6.5-cm increase in height resulted in lower levels of body mass index ( P < 0.001), triglycerides ( P < 0.001), non high-density (non-HDL) cholesterol ( P < 0.001), C-reactive protein ( P = 0.042), and systolic blood pressure ( P = 0.064) and higher levels of forced expiratory volume in 1 s and forced vital capacity ( P < 0.001 for both).
Conclusions: Taller individuals have a lower risk of CHD with potential explanations being that taller people have a better lung function and lower levels of body mass index, cholesterol and blood pressure.
© The Author 2015; all rights reserved. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association
Figures

References
-
- Waaler HT. Height, weight and mortality. The Norwegian experience. Acta med Scand Suppl 1984;679:1–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 090532/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/13/66/30442/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01HC55018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12019/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01WH32118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01HC55019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/16/30528/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH32100/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/8/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/672/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- N01HC55020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH22110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CZQ/1/38/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G0802432/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K006215/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG017644/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/005/23633/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH42107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC55016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/013/25942/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- N01WH42129/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N01104X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0500877/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01HC55021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/07/131/24254/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH32105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01WH32111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- G0902037/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CH/98001/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01HC55022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01WH32115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/98002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH44221/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH24152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC55015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/008/23674/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/10/12/28456/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

