In Vivo Programmed Gene Expression Based on Artificial Quorum Networks
- PMID: 25979894
- PMCID: PMC4495192
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01113-15
In Vivo Programmed Gene Expression Based on Artificial Quorum Networks
Abstract
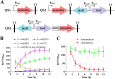
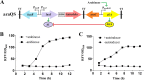
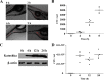
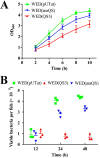
The quorum sensing (QS) system, as a well-functioning population-dependent gene switch, has been widely applied in many gene circuits in synthetic biology. In our work, an efficient cell density-controlled expression system (QS) was established via engineering of the Vibrio fischeri luxI-luxR quorum sensing system. In order to achieve in vivo programmed gene expression, a synthetic binary regulation circuit (araQS) was constructed by assembling multiple genetic components, including the quorum quenching protein AiiA and the arabinose promoter ParaBAD, into the QS system. In vitro expression assays verified that the araQS system was initiated only in the absence of arabinose in the medium at a high cell density. In vivo expression assays confirmed that the araQS system presented an in vivo-triggered and cell density-dependent expression pattern. Furthermore, the araQS system was demonstrated to function well in different bacteria, indicating a wide range of bacterial hosts for use. To explore its potential applications in vivo, the araQS system was used to control the production of a heterologous protective antigen in an attenuated Edwardsiella tarda strain, which successfully evoked efficient immune protection in a fish model. This work suggested that the araQS system could program bacterial expression in vivo and might have potential uses, including, but not limited to, bacterial vector vaccines.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

