Adjunctive raloxifene treatment improves attention and memory in men and women with schizophrenia
- PMID: 25980345
- PMCID: PMC4444978
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2015.11
Adjunctive raloxifene treatment improves attention and memory in men and women with schizophrenia
Abstract
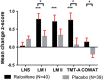
There is increasing clinical and molecular evidence for the role of hormones and specifically estrogen and its receptor in schizophrenia. A selective estrogen receptor modulator, raloxifene, stimulates estrogen-like activity in brain and can improve cognition in older adults. The present study tested the extent to which adjunctive raloxifene treatment improved cognition and reduced symptoms in young to middle-age men and women with schizophrenia. Ninety-eight patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder were recruited into a dual-site, thirteen-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of adjunctive raloxifene treatment in addition to their usual antipsychotic medications. Symptom severity and cognition in the domains of working memory, attention/processing speed, language and verbal memory were assessed at baseline, 6 and 13 weeks. Analyses of the initial 6-week phase of the study using a parallel groups design (with 39 patients receiving placebo and 40 receiving raloxifene) revealed that participants receiving adjunctive raloxifene treatment showed significant improvement relative to placebo in memory and attention/processing speed. There was no reduction in symptom severity with treatment compared with placebo. There were significant carryover effects, suggesting some cognitive benefits are sustained even after raloxifene withdrawal. Analysis of the 13-week crossover data revealed significant improvement with raloxifene only in attention/processing speed. This is the first study to show that daily, oral adjunctive raloxifene treatment at 120 mg per day has beneficial effects on attention/processing speed and memory for both men and women with schizophrenia. Thus, raloxifene may be useful as an adjunctive treatment for cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- Levine SZ, Rabinowitz J, Ascher-Svanum H, Faries DE, Lawson AH. Extent of attaining and maintaining symptom remission by antipsychotic medication in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia: evidence from the CATIE study. Schizophr Res. 2011;133:42–46. - PubMed
-
- Weickert TW, Goldberg TE.The course of cognitive impairment in patients with schizophreniaIn: Sharma T, Harvey P (eds). Cognition in Schizophrenia: Impairments, importance and treatment strategies Oxford University Press: New York, NY; 20003–15.
-
- Green MF. What are the functional consequences of neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1996;153:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Burke KC, Burke JD, Jr, Regier DA, Rae DS. Age at onset of selected mental disorders in five community populations. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990;47:511–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

