Long-term outcome in BRAF(V600E) melanoma patients treated with vemurafenib: Patterns of disease progression and clinical management of limited progression
- PMID: 25980594
- PMCID: PMC5087591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.04.010
Long-term outcome in BRAF(V600E) melanoma patients treated with vemurafenib: Patterns of disease progression and clinical management of limited progression
Abstract
Introduction: Vemurafenib induces tumour regression in most patients with BRAF(V600E)-mutant melanoma; eventually, most experience progressive disease (PD). Long-term follow-up of patients with BRAF(V600E) melanoma treated in the phase 1 vemurafenib trial is reported.
Methods: Patients received vemurafenib 240-1120 mg (dose escalation cohort) or 960 mg (extension cohort) orally twice daily. Clinical response was evaluated every 8 weeks by Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST). Patients with PD amenable to local therapy (surgery or radiotherapy) were allowed to continue vemurafenib after progression. Overall survival (OS) from time of treatment initiation and from PD was estimated. Sites of PD were recorded.
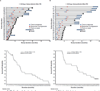
Results: Forty-eight patients (escalation cohort, n = 16; extension cohort, n = 32) received therapeutic doses of vemurafenib (⩾ 240 mg twice daily). Forty-four patients had PD by the time of this analysis and four remained progression free (follow-up time, 1.2-56.1 months). Median OS was 14 months (range, 1.2-56.1); 3- and 4-year melanoma-specific survival rate in the extension cohort was 26% and 19%, respectively. Median OS was 26.0 months (range, 7.7-56.1) among 20 patients who continued vemurafenib after local therapy. Median treatment duration beyond initial PD was 3.8 months (range, 1.1-26.6). In the extension cohort, six and five patients were alive after 3 and 4 years, respectively, on vemurafenib monotherapy.
Conclusions: Some patients with melanoma achieved long-term survival with vemurafenib monotherapy. Continuation of vemurafenib after PD might be beneficial in some patients because remaining disease might continue to respond to BRAF inhibition.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00405587.
Keywords: BRAF inhibitor; Metastatic melanoma; Vemurafenib.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures Nothing to disclose: Patrick Hwu.
Figures

References
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Goydos JS, Mann B, Kim HJ, et al. Detection of B-RAF and N-RAS mutations in human melanoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;200:362–370. - PubMed
-
- Libra M, Malaponte G, Navolanic PM, et al. Analysis of BRAF mutation in primary and metastatic melanoma. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1382–1384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

