Role and therapeutic potential of G-protein coupled receptors in breast cancer progression and metastases
- PMID: 25981295
- PMCID: PMC4784721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.011
Role and therapeutic potential of G-protein coupled receptors in breast cancer progression and metastases
Abstract
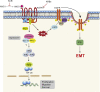
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise a large family of cell-surface receptors, which have recently emerged as key players in tumorigenesis, angiogenesis and metastasis. In this review, we discussed our current understanding of the many roles played by GPCRs in general, and particularly Angiotensin II type I receptor (AGTR1), a member of the seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein coupled receptor superfamily, and its significance in breast cancer progression and metastasis. We have also discussed different strategies for targeting AGTR1, and its ligand Angiotension II (Ang II), which might unravel unique opportunities for breast cancer prevention and treatment. For example, AGTR1 blockers (ARBs) which are already in clinical use for treating hypertension, merit further investigation as a therapeutic strategy for AGTR1-positive cancer patients and may have the potential to prevent Ang II-AGTR1 signalling mediated cancer pathogenesis and metastases.
Keywords: ACE; AGTR1; Breast cancer; GPCR; Metastases.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Amaya K., Ohta T., Kitagawa H., Kayahara M., Takamura H., Fujimura T., Nishimura G., Shimizu K., Miwa K. Angiotensin II activates MAP kinase and NF-kappaB through angiotensin II type I receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2004;25:849–856. - PubMed
-
- Asakura M., Kitakaze M., Takashima S., Liao Y., Ishikura F., Yoshinaka T., Ohmoto H., Node K., Yoshino K., Ishiguro H., Asanuma H., Sanada S., Matsumura Y., Takeda H., Beppu S., Tada M., Hori M., Higashiyama S. Cardiac hypertrophy is inhibited by antagonism of ADAM12 processing of HB-EGF: metalloproteinase inhibitors as a new therapy. Nat. Med. 2002;8:35–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

