Twice- rather than once-daily basal insulin is associated with better glycaemic control in Type 1 diabetes mellitus 12 months after skills-based structured education in insulin self-management
- PMID: 25982032
- PMCID: PMC4745019
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.12806
Twice- rather than once-daily basal insulin is associated with better glycaemic control in Type 1 diabetes mellitus 12 months after skills-based structured education in insulin self-management
Abstract
Aim: This study investigates the relationship between basal insulin regimen and glycaemic outcomes 12 months after skills-based structured education in the UK Dose Adjustment for Normal Eating (DAFNE) programme for Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Method: Retrospective analysis of data from 892 DAFNE participants from 11 UK centres.
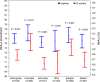
Results: Mean HbA1c 12 months after DAFNE was lower in those using twice- rather than once-daily basal insulin after correcting for differences in baseline HbA1c , age and duration of diabetes; difference -2 (95% CI -3 to -1) mmol/mol [-0.2 (-0.3 to -0.1)%], P = 0.009. The greatest fall in HbA1c of -5 (-7 to -3) mmol/mol [-0.4 (-0.6 to -0.3)%], P < 0.001 occurred in those with less good baseline control, HbA1c ≥ 58 mmol/mol, who switched from once- to twice-daily basal insulin. There was no difference in the 12-month HbA1c between users of glargine, detemir and NPH insulin after correcting for other variables. Relative risk of severe hypoglycaemia fell by 76% and ketoacidosis by 63% 12 months after DAFNE. The rate of severe hypoglycaemia fell from 0.82 to 0.23 events/patient year in twice-daily basal insulin users. In the group with greatest fall in HbA1c , the estimated relative risk for severe hypoglycaemia in twice-daily basal insulin users versus once daily at 12 months was 1.72 (0.88-3.36, P = 0.110).
Conclusion: After structured education in adults with Type 1 diabetes mellitus, use of basal insulin twice rather than once daily was associated with lower HbA1c , independent of insulin type, with significant reductions in severe hypoglycaemia and ketoacidosis in all groups.
© 2015 The Authors. Diabetic Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Diabetes UK.
Figures
References
-
- Dose Adjustment for Normal Eating. Available at www.dafne.uk.com Last accessed 12 November 2014.
-
- Lawton J, Rankin AD, Cooke D, Elliott J, Amiel SA, Heller S. Patients’ experiences of adjusting insulin doses when implementing flexible intensive insulin therapy: a longitudinal, qualitative investigation. Diabet Res Clin Pract 2012; 98: 236–242. - PubMed
-
- Mülhauser I, Jorgens V, Berger M, Graninger W, Gurtler W, Hornke L et al Bicentric evaluation of a teaching and treatment programme for type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients: improvement of metabolic control and other measures of diabetes care for up to 22 months. Diabetologia 1983; 25: 470–476. - PubMed
-
- Oliver L, Thompson G. The DAFNE Collaborative: experiences of developing and delivering an evidence based quality assured programme for people with Type 1 diabetes. Pract Diabetes Int 2009; 26: 371–377.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

