IFNA2: The prototypic human alpha interferon
- PMID: 25982860
- PMCID: PMC5629289
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.087
IFNA2: The prototypic human alpha interferon
Abstract
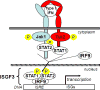
The human interferon α2 (IFNα2) was the first highly active IFN subtype to be cloned in the early eighties. It was also the first IFN and the first cytokine to be produced and commercialized by the pharmaceutical industry. Ipso facto it became the favorite IFNα subtype for academic researchers. For this fortunate reason IFNα2 has been at the origin of most discoveries related to the mechanism of action of type I interferons.
Keywords: Cytokine; Interferon α2; Type I interferon.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bidwell BN, Slaney CY, Withana NP, Forster S, Cao Y, Loi S, Andrews D, Mikeska T, Mangan NE, Samarajiwa SA, de Weerd NA, Gould J, Argani P, Moller A, Smyth MJ, Anderson RL, Hertzog PJ, Parker BS. Silencing of Irf7 pathways in breast cancer cells promotes bone metastasis through immune escape. Nat Med. 2012;18:1224–31. - PubMed
-
- Bogunovic D, Byun M, Durfee LA, Abhyankar A, Sanal O, Mansouri D, Salem S, Radovanovic I, Grant AV, Adimi P, Mansouri N, Okada S, Bryant VL, Kong XF, Kreins A, Velez MM, Boisson B, Khalilzadeh S, Ozcelik U, Darazam IA, Schoggins JW, Rice CM, Al-Muhsen S, Behr M, Vogt G, Puel A, Bustamante J, Gros P, Huibregtse JM, Abel L, Boisson-Dupuis S, Casanova JL. Mycobacterial disease and impaired IFN-gamma immunity in humans with inherited ISG15 deficiency. Science. 2012;337:1684–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

