Risk factors and diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of hip in children
- PMID: 25983450
- PMCID: PMC3872792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2011.11.001
Risk factors and diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of hip in children
Abstract
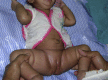
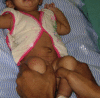
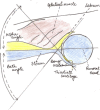
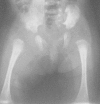
Developmental dysplasia of hip (DDH) is one entity one occasionally comes across while in a busy orthopaedic or paediatric outpatient department. The knowledge of risk factors and awareness of the condition is must for every orthopaedic surgeon and paediatrician as well lest the diagnosis will be missed. An early diagnosis can alter the prognosis of the disease and prevent late disabilities.
Keywords: Congenital dislocation of hip; Developmental dysplasia of hip; Diagnosis; Risk factors.
Figures


References
-
- Sankar W.N., Weiss J., Skaggs D.L. Orthopaedic conditions in the newborn. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(2):112–122. - PubMed
-
- AIUM practice guideline for the performance of an ultrasound examination for detection and assessment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28(1):114–119. - PubMed
-
- Davies S.J., Walker G. Problems in the early recognition of hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984;66:479–484. - PubMed
-
- Klisic P.J. Congenital dislocation of the hip– a misleading term: a brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71:136. - PubMed
-
- Sewell M.D., Rosendahl K., Eastwood D.M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. BMJ. 2009 Nov 24;339:b4454. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

