mHealth in Urology: A Review of Experts' Involvement in App Development
- PMID: 25984916
- PMCID: PMC4436179
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125547
mHealth in Urology: A Review of Experts' Involvement in App Development
Abstract
Introduction: Smartphones are increasingly playing a role in healthcare and previous studies assessing medical applications (apps) have raised concerns about lack of expert involvement and low content accuracy. However, there are no such studies in Urology. We reviewed Urology apps with the aim of assessing the level of participation of healthcare professionals (HCP) and scientific Urology associations in their development.
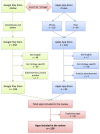
Material and methods: A systematic search was performed on PubMed, Apple's App Store and Google's Play Store, for Urology apps, available in English. Apps were reviewed by three graders to determine the app's platform, target customer, developer, app type, app category, price and the participation of a HCP or a scientific Urology association in the development.
Results: The search yielded 372 apps, of which 150 were specific for Urology. A fifth of all apps had no HCP involvement (20.7%) and only a third had been developed with a scientific Urology association (34.7%). The lowest percentage of HCP (13.4%) and urological association (1.9%) involvement was in apps designed for the general population. Furthermore, there was no contribution from an Urology society in "Electronic Medical Record" nor in "Patient Information" apps. A limitation of the study is that only Android and iOS apps were reviewed.
Conclusions: Despite the increasing Mobile Health (mHealth) market, this is the first study that demonstrates the lack of expert participation in the design of Urology apps, particularly in apps designed for the general public. Until clear regulation is enforced, the urological community should help regulate app development. Maintaining a register of certified apps or issuing an official scientific seal of approval could improve overall app quality. We propose that urologists become stakeholders in mHealth, shaping future app design and promoting peer-review app validation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kwok R (2013) Mobile apps: A conference in your pocket. Nature 498: 20 June 395–397. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization; (2011) mHealth: New horizons for health through mobile technologies (Global Observatory for eHealth series—Volume 3). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
-
- Research2Guidance (2013) The mobile health global market report 2013–2017: the commercialisation of mHealth apps (Vol. 3). Available: http://www.research2guidance.com/shop/index.php/downloadable/download/sa.... Accessed September 2014.
-
- Apple HealthKit. Available: https://developer.apple.com/healthkit/. Accessed September 2014.
-
- Google Fit. Available: https://developers.google.com/fit/. Accessed September 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

