A FYVE zinc finger domain protein specifically links mRNA transport to endosome trafficking
- PMID: 25985087
- PMCID: PMC4466420
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.06041
A FYVE zinc finger domain protein specifically links mRNA transport to endosome trafficking
Abstract
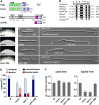
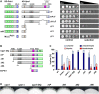
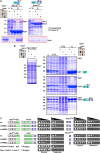
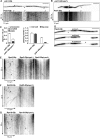
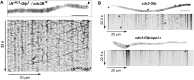
An emerging theme in cellular logistics is the close connection between mRNA and membrane trafficking. A prominent example is the microtubule-dependent transport of mRNAs and associated ribosomes on endosomes. This coordinated process is crucial for correct septin filamentation and efficient growth of polarised cells, such as fungal hyphae. Despite detailed knowledge on the key RNA-binding protein and the molecular motors involved, it is unclear how mRNAs are connected to membranes during transport. Here, we identify a novel factor containing a FYVE zinc finger domain for interaction with endosomal lipids and a new PAM2-like domain required for interaction with the MLLE domain of the key RNA-binding protein. Consistently, loss of this FYVE domain protein leads to specific defects in mRNA, ribosome, and septin transport without affecting general functions of endosomes or their movement. Hence, this is the first endosomal component specific for mRNP trafficking uncovering a new mechanism to couple mRNPs to endosomes.
Keywords: FYVE; PAM2; RRM; Ustilago maydis; cell biology; endosome; infectious disease; mRNA transport; microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures














References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

