Dysfunctional SEMA3E signaling underlies gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron deficiency in Kallmann syndrome
- PMID: 25985275
- PMCID: PMC4497752
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI78448
Dysfunctional SEMA3E signaling underlies gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron deficiency in Kallmann syndrome
Abstract
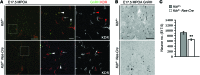
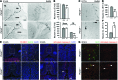
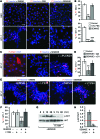
Individuals with an inherited deficiency in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) have impaired sexual reproduction. Previous genetic linkage studies and sequencing of plausible gene candidates have identified mutations associated with inherited GnRH deficiency, but the small number of affected families and limited success in validating candidates have impeded genetic diagnoses for most patients. Using a combination of exome sequencing and computational modeling, we have identified a shared point mutation in semaphorin 3E (SEMA3E) in 2 brothers with Kallmann syndrome (KS), which causes inherited GnRH deficiency. Recombinant wild-type SEMA3E protected maturing GnRH neurons from cell death by triggering a plexin D1-dependent (PLXND1-dependent) activation of PI3K-mediated survival signaling. In contrast, recombinant SEMA3E carrying the KS-associated mutation did not protect GnRH neurons from death. In murine models, lack of either SEMA3E or PLXND1 increased apoptosis of GnRH neurons in the developing brain, reducing innervation of the adult median eminence by GnRH-positive neurites. GnRH neuron deficiency in male mice was accompanied by impaired testes growth, a characteristic feature of KS. Together, these results identify SEMA3E as an essential gene for GnRH neuron development, uncover a neurotrophic function for SEMA3E in the developing brain, and elucidate SEMA3E/PLXND1/PI3K signaling as a mechanism that prevents GnRH neuron deficiency.
Figures







Comment in
-
Fertility and fragrance: another cause of Kallmann syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2275-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI82061. Epub 2015 May 18. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25985271 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Fertility and fragrance: another cause of Kallmann syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2275-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI82061. Epub 2015 May 18. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25985271 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3d and semaphorin 3e direct endothelial motility through distinct molecular signaling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 27;289(26):17971-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.544833. Epub 2014 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24825896 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3E-Plexin-D1 signaling regulates VEGF function in developmental angiogenesis via a feedback mechanism.Genes Dev. 2011 Jul 1;25(13):1399-411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2042011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21724832 Free PMC article.
-
Kallmann syndrome and idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: The role of semaphorin signaling on GnRH neurons.Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;182:307-315. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819973-2.00022-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34266601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[GnRH deficiency: new insights from genetics].J Soc Biol. 2004;198(1):80-7. J Soc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15146960 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms underlying pre- and postnatal development of the vomeronasal organ.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(12):5069-5082. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03829-3. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33871676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A recessive PRDM13 mutation results in congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and cerebellar hypoplasia.J Clin Invest. 2021 Dec 15;131(24):e141587. doi: 10.1172/JCI141587. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34730112 Free PMC article.
-
Withdrawn: Discovering Genes Essential to the Hypothalamic Regulation of Human Reproduction Using a Human Disease Model: Adjusting to Life in the "-Omics" Era.Endocr Rev. 2016 Feb;2016(1):4-22. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1045.2016.1.test. Endocr Rev. 2016. Retraction in: Endocr Rev. 2020 Dec 1;41(6):bnaa019. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa019. PMID: 27454361 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Mammalian puberty: a fly perspective.FEBS J. 2023 Jan;290(2):359-369. doi: 10.1111/febs.16534. Epub 2022 Jun 21. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 35607827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the Genetics of Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017 Dec 30;9(Suppl 2):113-122. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.2017.S010. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 29280744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cariboni A, Davidson K, Rakic S, Maggi R, Parnavelas JG, Ruhrberg C. Defective gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron migration in mice lacking SEMA3A signalling through NRP1 and NRP2: implications for the aetiology of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(2):336–344. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq468. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

