Identification, characterization and antibiotic resistance of bacterial isolates obtained from waterpipe device hoses
- PMID: 25985311
- PMCID: PMC4454957
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120505108
Identification, characterization and antibiotic resistance of bacterial isolates obtained from waterpipe device hoses
Abstract
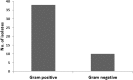
The general lack of knowledge about the health effects of waterpipe smoking is among the reasons for its global spread. In this study, bacterial contamination of waterpipe hoses was investigated. Twenty hoses were collected from waterpipe cafés and screened for bacterial pathogens using standard culture and isolation techniques. Additionally, resistance of isolated bacteria to common antibiotics was determined by identifying the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of each isolate. Forty eight bacterial isolates were detected. Isolates included both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens from species that included Micrococcus (12), Corynebacterium (13) and Bacillus (9). In addition, some of the detected pathogens were found to be resistant to aztreonam (79%), cefixime (79%), norfloxacin, amoxicillin (47%), clarithromycin (46%) and enrofloxacin (38%). In conclusion, the hose of the waterpipe device is a good environment for the growth of bacterial pathogens, which can then be transmitted to users.
Keywords: antibiotics resistance; bacteria; hose; isolates; waterpipe.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in Toronto: an 11-year review.Ophthalmology. 2012 Sep;119(9):1785-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.03.031. Epub 2012 May 23. Ophthalmology. 2012. PMID: 22627118
-
Ocular Pathogens and Antibiotic Sensitivity in Bacterial Keratitis Isolates at King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, 2011 to 2014.Cornea. 2016 Jun;35(6):789-94. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000844. Cornea. 2016. PMID: 27078003
-
Bacteriologic profile and antibiogram of blood culture isolates from a children's hospital in Kabul.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014 Jun;24(6):396-399. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014. PMID: 24953929
-
Microbiological spectrum and antibiotic sensitivity in endophthalmitis: a 25-year review.Ophthalmology. 2014 Aug;121(8):1634-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Ophthalmology. 2014. PMID: 24702755 Review.
-
The emergence of clinical resistance to tigecycline.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Feb;41(2):110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.09.005. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23127485 Review.
Cited by
-
Health Effects of Waterpipe Tobacco Use: Getting the Public Health Message Just Right.Tob Use Insights. 2017 Apr 11;10:1179173X17696055. doi: 10.1177/1179173X17696055. eCollection 2017. Tob Use Insights. 2017. PMID: 28579844 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of hookah/waterpipe smoking on general health and the cardiovascular system.Environ Health Prev Med. 2019 Sep 14;24(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12199-019-0811-y. Environ Health Prev Med. 2019. PMID: 31521105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioaerosols in the waterpipe cafés: genera, levels, and factors influencing their concentrations.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jul;26(20):20297-20307. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05413-6. Epub 2019 May 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31098913
-
Waterpipe tobacco smoking impact on public health: implications for policy.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2015 Aug 27;8:121-9. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S68267. eCollection 2015. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2015. PMID: 26346473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in oral microbial flora induced by waterpipe tobacco smoking.Int J Gen Med. 2018 Feb 2;11:47-54. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S150553. eCollection 2018. Int J Gen Med. 2018. PMID: 29440924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jradi H., Wewers M.E., Pirie P.R., Binkley P.F., Ferketich K. Cigarette and waterpipe smoking associated knowledge and behaviour among medical students in Lebanon. East Mediterr. Health J. 2013;19:861–868. - PubMed
-
- Obeidat S.R., Khabour O.F., Alzoubi K.H., Mahasneh A.M., Bibars A.R., Khader Y.S., Alsa’di A. Prevalence, social acceptance, and awareness of waterpipe smoking among dental university students: A cross sectional survey conducted in Jordan. BMC Res. Notes. 2014;7 doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-832. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical