Baroreflex activation in conscious rats modulates the joint inflammatory response via sympathetic function
- PMID: 25986215
- PMCID: PMC7023897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.05.002
Baroreflex activation in conscious rats modulates the joint inflammatory response via sympathetic function
Abstract
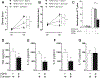
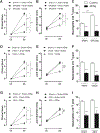
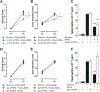
The baroreflex is a critical physiological mechanism controlling cardiovascular function by modulating both the sympathetic and parasympathetic activities. Here, we report that electrical activation of the baroreflex attenuates joint inflammation in experimental arthritis induced by the administration of zymosan into the femorotibial cavity. Baroreflex activation combined with lumbar sympathectomy, adrenalectomy, celiac subdiaphragmatic vagotomy or splenectomy dissected the mechanisms involved in the inflammatory modulation, highlighting the role played by sympathetic inhibition in the attenuation of joint inflammation. From the immunological standpoint, baroreflex activation attenuates neutrophil migration and the synovial levels of inflammatory cytokines including TNF, IL-1β and IL-6, but does not affect the levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. The anti-inflammatory effects of the baroreflex system are not mediated by IL-10, the vagus nerve, adrenal glands or the spleen, but by the inhibition of the sympathetic drive to the knee. These results reveal a novel physiological neuronal network controlling peripheral local inflammation.
Keywords: Baroreflex; Inflammation; Neuroimmunomodulation; Parasympathetic activity; Sympathetic activity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akine A, Suzuka H, Hayashida Y, Kato Y, 2001. Effects of ketamine and propofol on autonomic cardiovascular function in chronically instrumented rats. Auton. Neurosci. 87, 201–208. - PubMed
-
- Bassani T, Bari V, Marchi A, Wu MA, Baselli G, Citerio G, Beda A, de Abreu MG, Güldner A, Guzzetti S, Porta A, 2013. Coherence analysis overestimates the role of baroreflex in governing the interactions between heart period and systolic arterial pressure variabilities during general anesthesia. Auton. Neurosci 178, 83–88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassi GS, Kanashiro A, Santin FM, de Souza GEP, Nobre MJ, Coimbra NC, 2012. Lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behaviour evaluated in different models of anxiety and innate fear in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol 110, 359–369. - PubMed
-
- Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ, 2000. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405, 458–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

