Effects of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition in Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients: The Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition for Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients (EXACT-HF) Study
- PMID: 25986447
- PMCID: PMC4438785
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014536
Effects of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition in Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients: The Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition for Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients (EXACT-HF) Study
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress may contribute to heart failure (HF) progression. Inhibiting xanthine oxidase in hyperuricemic HF patients may improve outcomes.
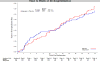
Methods and results: We randomly assigned 253 patients with symptomatic HF, left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%, and serum uric acid levels ≥9.5 mg/dL to receive allopurinol (target dose, 600 mg daily) or placebo in a double-blind, multicenter trial. The primary composite end point at 24 weeks was based on survival, worsening HF, and patient global assessment. Secondary end points included change in quality of life, submaximal exercise capacity, and left ventricular ejection fraction. Uric acid levels were significantly reduced with allopurinol in comparison with placebo (treatment difference, -4.2 [-4.9, -3.5] mg/dL and -3.5 [-4.2, -2.7] mg/dL at 12 and 24 weeks, respectively, both P<0.0001). At 24 weeks, there was no significant difference in clinical status between the allopurinol- and placebo-treated patients (worsened 45% versus 46%, unchanged 42% versus 34%, improved 13% versus 19%, respectively; P=0.68). At 12 and 24 weeks, there was no significant difference in change in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire scores or 6-minute walk distances between the 2 groups. At 24 weeks, left ventricular ejection fraction did not change in either group or between groups. Rash occurred more frequently with allopurinol (10% versus 2%, P=0.01), but there was no difference in serious adverse event rates between the groups (20% versus 15%, P=0.36).
Conclusions: In high-risk HF patients with reduced ejection fraction and elevated uric acid levels, xanthine oxidase inhibition with allopurinol failed to improve clinical status, exercise capacity, quality of life, or left ventricular ejection fraction at 24 weeks.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00987415.
Keywords: allopurinol; clinical trial; heart failure; xanthine oxidase.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



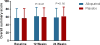
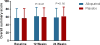

Comment in
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors in heart failure: where do we go from here?Circulation. 2015 May 19;131(20):1741-4. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016379. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25986446 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tsutsui H, Kinugawa S, Matsushima S. Oxidative stress and heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301:H2181–2190. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Doehner W, Rauchhaus M, Sharma R, Francis D, Knosalla C, Davos CH, Cicoira M, Shamim W, Kemp M, Segal R, Osterziel KJ, Leyva F, Hetzer R, Ponikowski P, Coats AJ. Uric acid and survival in chronic heart failure: Validation and application in metabolic, functional, and hemodynamic staging. Circulation. 2003;107:1991–1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 HL084890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL084861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110297/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U109HL110337/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110337/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 8 U54 MD007588/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007588/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL084890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL084889/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL084904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL084931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110302/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110302/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110297/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL084891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL110312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL113777/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL084904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084889/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL110309/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

