Biochemical Characterization of Mycobacterium smegmatis RnhC (MSMEG_4305), a Bifunctional Enzyme Composed of Autonomous N-Terminal Type I RNase H and C-Terminal Acid Phosphatase Domains
- PMID: 25986906
- PMCID: PMC4518832
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00268-15
Biochemical Characterization of Mycobacterium smegmatis RnhC (MSMEG_4305), a Bifunctional Enzyme Composed of Autonomous N-Terminal Type I RNase H and C-Terminal Acid Phosphatase Domains
Abstract
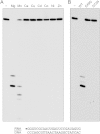
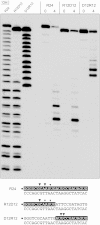
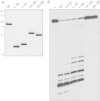
Mycobacterium smegmatis encodes several DNA repair polymerases that are adept at incorporating ribonucleotides, which raises questions about how ribonucleotides in DNA are sensed and removed. RNase H enzymes, of which M. smegmatis encodes four, are strong candidates for a surveillance role. Here, we interrogate the biochemical activity and nucleic acid substrate specificity of M. smegmatis RnhC, a bifunctional RNase H and acid phosphatase. We report that (i) the RnhC nuclease is stringently specific for RNA:DNA hybrid duplexes; (ii) RnhC does not selectively recognize and cleave DNA-RNA or RNA-DNA junctions in duplex nucleic acid; (iii) RnhC cannot incise an embedded monoribonucleotide or diribonucleotide in duplex DNA; (iv) RnhC can incise tracts of 4 or more ribonucleotides embedded in duplex DNA, leaving two or more residual ribonucleotides at the cleaved 3'-OH end and at least one or two ribonucleotides on the 5'-PO4 end; (v) the RNase H activity is inherent in an autonomous 140-amino-acid (aa) N-terminal domain of RnhC; and (vi) the C-terminal 211-aa domain of RnhC is an autonomous acid phosphatase. The cleavage specificity of RnhC is clearly distinct from that of Escherichia coli RNase H2, which selectively incises at an RNA-DNA junction. Thus, we classify RnhC as a type I RNase H. The properties of RnhC are consistent with a role in Okazaki fragment RNA primer removal or in surveillance of oligoribonucleotide tracts embedded in DNA but not in excision repair of single misincorporated ribonucleotides.
Importance: RNase H enzymes help cleanse the genome of ribonucleotides that are present either as ribotracts (e.g., RNA primers) or as single ribonucleotides embedded in duplex DNA. Mycobacterium smegmatis encodes four RNase H proteins, including RnhC, which is characterized in this study. The nucleic acid substrate and cleavage site specificities of RnhC are consistent with a role in initiating the removal of ribotracts but not in single-ribonucleotide surveillance. RnhC has a C-terminal acid phosphatase domain that is functionally autonomous of its N-terminal RNase H catalytic domain. RnhC homologs are prevalent in Actinobacteria.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

