Vitamin D in addition to peg-interferon-alpha/ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: ANRS-HC25-VITAVIC study
- PMID: 25987791
- PMCID: PMC4427690
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5647
Vitamin D in addition to peg-interferon-alpha/ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: ANRS-HC25-VITAVIC study
Abstract
Aim: To investigate if correction of hypovitaminosis D before initiation of Peg-interferon-alpha/ribavirin (PegIFN/RBV) therapy could improve the efficacy of PegIFN/RBV in previously null-responder patients with chronic genotype 1 or 4 hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
Methods: Genotype 1 or 4 HCV-infected patients with null response to previous PegIFN/RBV treatment and with hypovitaminosis D (< 30 ng/mL) prospectively received cholecalciferol 100000 IU per week for 4 wk [from week -4 (W-4) to W0], followed by 100000 IU per month in combination with PegIFN/RBV for 12 mo (from W0 to W48). The primary outcome was the rate of early virological response defined by an HCV RNA < 12 IU/mL after 12 wk PegIFN/RBV treatment.
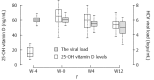
Results: A total of 32 patients were included, 19 (59%) and 13 (41%) patients were HCV genotype 1 and 4, respectively. The median baseline vitamin D level was 15 ng/mL (range: 7-28). In modified intention-to-treat analysis, 29 patients who received at least one dose of PegIFN/RBV were included in the analysis. All patients except one normalized their vitamin D serum levels. The rate of early virologic response was 0/29 (0%). The rate of HCV RNA < 12 IU/mL after 24 wk of PegIFN/RBV was 1/27 (4%). The safety profile was favorable.
Conclusion: Addition of vitamin D to PegIFN/RBV does not improve the rate of early virologic response in previously null-responders with chronic genotype 1 or 4 HCV infection.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01226446.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis; Hepatitis C virus; Pegylated interferon; Ribavirin; Vitamin D.
Figures
References
-
- McHutchison JG, Manns MP, Muir AJ, Terrault NA, Jacobson IM, Afdhal NH, Heathcote EJ, Zeuzem S, Reesink HW, Garg J, et al. Telaprevir for previously treated chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1292–1303. - PubMed
-
- Jensen DM, Marcellin P, Freilich B, Andreone P, Di Bisceglie A, Brandão-Mello CE, Reddy KR, Craxi A, Martin AO, Teuber G, et al. Re-treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C who do not respond to peginterferon-alpha2b: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:528–540. - PubMed
-
- McHutchison JG, Everson GT, Gordon SC, Jacobson IM, Sulkowski M, Kauffman R, McNair L, Alam J, Muir AJ. Telaprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1827–1838. - PubMed
-
- Hézode C, Forestier N, Dusheiko G, Ferenci P, Pol S, Goeser T, Bronowicki JP, Bourlière M, Gharakhanian S, Bengtsson L, et al. Telaprevir and peginterferon with or without ribavirin for chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1839–1850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical