Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition
- PMID: 25987957
- PMCID: PMC4434080
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.598
Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is increasing at an alarming rate and has become a global challenge. Insulin resistance in target tissues and a relative deficiency of insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells are the major features of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Chronic low-grade inflammation in T2D has given an impetus to the field of immuno-metabolism linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Many factors advocate a causal link between metabolic stress and inflammation. Numerous cellular factors trigger inflammatory signalling cascades, and as a result T2D is at the moment considered an inflammatory disorder triggered by disordered metabolism. Cellular mechanisms like activation of Toll-like receptors, Endoplasmic Reticulum stress, and inflammasome activation are related to the nutrient excess linking pathogenesis and progression of T2D with inflammation. This paper aims to systematically review the metabolic profile and role of various inflammatory pathways in T2D by capturing relevant evidence from various sources. The perspectives include suggestions for the development of therapies involving the shift from metabolic stress to homeostasis that would favour insulin sensitivity and survival of pancreatic β-cells in T2D.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Diabetes mellitus; Inflammation; Insulin resistance; β-cell dysfunction.
Figures
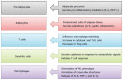

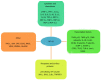
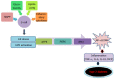
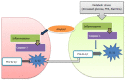
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2013. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
-
- Nolan CJ, Damm P, Prentki M. Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. Lancet. 2011;378:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:102–110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

