Secretory autophagy
- PMID: 25988755
- PMCID: PMC4529791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.04.016
Secretory autophagy
Abstract
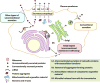
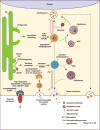
Autophagy, once viewed exclusively as a cytoplasmic auto-digestive process, has its less intuitive but biologically distinct non-degradative roles. One manifestation of these functions of the autophagic machinery is the process termed secretory autophagy. Secretory autophagy facilitates unconventional secretion of the cytosolic cargo such as leaderless cytosolic proteins, which unlike proteins endowed with the leader (N-terminal signal) peptides cannot enter the conventional secretory pathway normally operating via the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Secretory autophagy may also export more complex cytoplasmic cargo and help excrete particulate substrates. Autophagic machinery and autophagy as a process also affect conventional secretory pathways, including the constitutive and regulated secretion, as well as promote alternative routes for trafficking of integral membrane proteins to the plasma membrane. Thus, autophagy and autophagic factors are intimately intertwined at many levels with secretion and polarized sorting in eukaryotic cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Rabouille C, et al. Diversity in unconventional protein secretion. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:5251–5255. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Schekman R. Cell biology. Unconventional secretion, unconventional solutions. Science. 2013;340:559–561. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, et al. The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:107–132. - PubMed
-
- Rogov V, et al. Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 2014;53:167–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

