Application of high-dimensional feature selection: evaluation for genomic prediction in man
- PMID: 25988841
- PMCID: PMC4437376
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10312
Application of high-dimensional feature selection: evaluation for genomic prediction in man
Abstract
In this study, we investigated the effect of five feature selection approaches on the performance of a mixed model (G-BLUP) and a Bayesian (Bayes C) prediction method. We predicted height, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) and body mass index (BMI) within 2,186 Croatian and into 810 UK individuals using genome-wide SNP data. Using all SNP information Bayes C and G-BLUP had similar predictive performance across all traits within the Croatian data, and for the highly polygenic traits height and BMI when predicting into the UK data. Bayes C outperformed G-BLUP in the prediction of HDL, which is influenced by loci of moderate size, in the UK data. Supervised feature selection of a SNP subset in the G-BLUP framework provided a flexible, generalisable and computationally efficient alternative to Bayes C; but careful evaluation of predictive performance is required when supervised feature selection has been used.
Figures
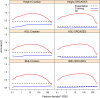
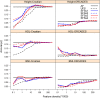
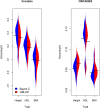
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I014144/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/276/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

