Briakinumab for treatment of Crohn's disease: results of a randomized trial
- PMID: 25989338
- PMCID: PMC4450894
- DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000366
Briakinumab for treatment of Crohn's disease: results of a randomized trial
Abstract
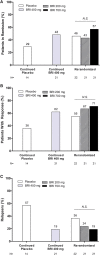
Background: This study assessed the efficacy and safety of briakinumab, a human anti-IL-12/23p40 monoclonal antibody, compared with placebo for the induction and maintenance of remission in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease.
Methods: In this phase 2b, multicenter, double-blind, parallel group study, 246 patients stratified by prior tumor necrosis factor-antagonist use and response, were randomized (1:1:1:3) to 4 intravenous induction regimens: placebo, 200, 400, or 700 mg briakinumab, at weeks 0/4/8. At week 12, responders in the placebo or 400-mg induction groups entered the maintenance phase with the same regimen, whereas responders in the 700-mg induction group were rerandomized (1:1:1) to receive placebo, 200, or 700 mg briakinumab at weeks 12/16/20. At week 24, patients in remission stopped receiving study drug (withdrawal phase) until relapse. Patients experiencing relapse, nonresponders, and nonremitters could enter the open-label phase.
Results: The primary end point of clinical remission at week 6 was not met. There were numerically greater rates of remission and response at 6, 12, or 24 weeks in patients treated with briakinumab. The safety and tolerability profile of briakinumab was similar in the induction and maintenance phases of the trial.
Conclusions: Briakinumab showed a similar safety and tolerability profile to placebo in the induction and maintenance phases, and comparable rates of serious adverse events, adverse events leading to discontinuation, and malignancy. These data provide support for the potential efficacy of briakinumab and other IL-12/23 inhibitors in the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn's disease.
Figures



References
-
- Baumgart DC, Carding SR. Inflammatory bowel disease: cause and immunobiology. Lancet. 2007;369:1627–1640. - PubMed
-
- Baert FJ, Rutgeerts PR. Anti-TNF strategies in Crohn's disease: mechanisms, clinical effects, indications. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1999;14:47–51. - PubMed
-
- Sarra M, Pallone F, Macdonald TT, et al. IL-23/IL-17 axis in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:1808–1813. - PubMed
-
- Fuss IJ, Becker C, Yang Z, et al. Both IL-12p70 and IL-23 are synthesized during active Crohn's disease and are down-regulated by treatment with anti-IL-12 p40 monoclonal antibody. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12:9–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

