Stigma as a barrier to treatment for child acute malnutrition in Marsabit County, Kenya
- PMID: 25989353
- PMCID: PMC6860141
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12198
Stigma as a barrier to treatment for child acute malnutrition in Marsabit County, Kenya
Abstract
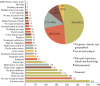
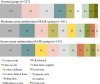
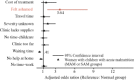
Acute malnutrition affects millions of children each year, yet global coverage of life-saving treatment through the community-based management of acute malnutrition (CMAM) is estimated to be below 15%. We investigated the potential role of stigma as a barrier to accessing CMAM. We surveyed caregivers bringing children to rural health facilities in Marsabit County, Kenya, divided into three strata based on the mid-upper arm circumference of the child: normal status (n = 327), moderate acute malnutrition (MAM, n = 241) and severe acute malnutrition (SAM, n = 143). We used multilevel mixed effects logistic regression to estimate the odds of reporting shame as a barrier to accessing health care. We found that the most common barriers to accessing child health care were those known to be universally problematic: women's time and labour constraints. These constituted the top five most frequently reported barriers regardless of child acute malnutrition status. In contrast, the odds of reporting shame as a barrier were 3.64 (confidence interval: 1.66-8.03, P < 0.05) times higher in caregivers of MAM and SAM children relative to those of normal children. We conclude that stigma is an under-recognized barrier to accessing CMAM and may constrain programme coverage. In light of the large gap in coverage of CMAM, there is an urgent need to understand the sources of acute malnutrition-associated stigma and adopt effective means of de-stigmatization.
Keywords: access; acute malnutrition; community-based management of acute malnutrition; stigma.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barton P.L. (2010) Understanding the US Health Service System, 4th edn Health Administration Press: Chicago.
-
- Baskind R. & Birbeck G.L. (2005) Epilepsy‐associated stigma in sub‐Saharan Africa: the social landscape of a disease. Epilepsy & Behavior 7 (1), 68–73. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta Z.A., Ahmed T., Black R.E., Cousens S., Dewey K., Guigliani E. et al (2005) Effective international action against undernutrition: why has it proven so difficult and what can be done to accelerate progress? The Lancet 368 (9551), 1992–2000. - PubMed
-
- Black R.E., Victora C.G., Walker S.P., Bhutta Z.A., Christian P., de Onis M. et al (2013) Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low‐income and middle‐income countries. The Lancet 382, 427–451. - PubMed
-
- Bond V. (2006) Stigma when there is no other option: understanding how poverty fuels discrimination toward people living with HIV in Zambia In: AIDS, Poverty, and Hunger: Challenges and Responses (ed. Gillespie S.), pp. 181–197. International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC. AIDS
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

