Proteins that bind regulatory regions identified by histone modification chromatin immunoprecipitations and mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25990348
- PMCID: PMC4455091
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8155
Proteins that bind regulatory regions identified by histone modification chromatin immunoprecipitations and mass spectrometry
Abstract
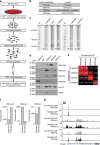
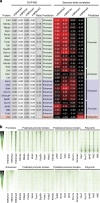
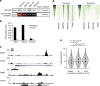
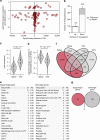
The locations of transcriptional enhancers and promoters were recently mapped in many mammalian cell types. Proteins that bind those regulatory regions can determine cell identity but have not been systematically identified. Here we purify native enhancers, promoters or heterochromatin from embryonic stem cells by chromatin immunoprecipitations (ChIP) for characteristic histone modifications and identify associated proteins using mass spectrometry (MS). 239 factors are identified and predicted to bind enhancers or promoters with different levels of activity, or heterochromatin. Published genome-wide data indicate a high accuracy of location prediction by ChIP-MS. A quarter of the identified factors are important for pluripotency and includes Oct4, Esrrb, Klf5, Mycn and Dppa2, factors that drive reprogramming to pluripotent stem cells. We determined the genome-wide binding sites of Dppa2 and find that Dppa2 operates outside the classical pluripotency network. Our ChIP-MS method provides a detailed read-out of the transcriptional landscape representative of the investigated cell type.
Figures

References
-
- Chen X. et al.. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell 133, 1106–1117 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K. & Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

