One-year postoperative resource utilization in sarcopenic patients
- PMID: 25990695
- PMCID: PMC4604009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.04.074
One-year postoperative resource utilization in sarcopenic patients
Abstract
Background: It is well established that sarcopenic patients are at higher risk of postoperative complications and short-term health care utilization. Less well understood is how these patients fare over the long term after surviving the immediate postoperative period. We explored costs over the first postoperative year among sarcopenic patients.
Methods: We identified 1279 patients in the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative database who underwent inpatient elective surgery at a single institution from 2006-2011. Sarcopenia, defined by gender-stratified tertiles of lean psoas area, was determined from preoperative computed tomography scans using validated analytic morphomics. Data were analyzed to assess sarcopenia's relationship to costs, readmissions, discharge location, intensive care unit admissions, hospital length of stay, and mortality. Multivariate models were adjusted for patient demographics and surgical risk factors.
Results: Sarcopenia was independently associated with increased adjusted costs at 30, 90, and 180 but not 365 d. The difference in adjusted postsurgical costs between sarcopenic and nonsarcopenic patients was $16,455 at 30 d and $14,093 at 1 y. Sarcopenic patients were more likely to be discharged somewhere other than home (P < 0.001). Sarcopenia was not an independent predictor of increased readmission rates in the postsurgical year.
Conclusions: The effects of sarcopenia on health care costs are concentrated in the immediate postoperative period. It may be appropriate to allocate additional resources to sarcopenic patients in the perioperative setting to reduce the incidence of negative postoperative outcomes.
Keywords: Cost; Discharge disposition; Health care utilization; Morphomics; Readmissions; Sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
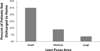

References
-
- Zembroń-Łacny A, Dziubek W, Rogowski Ł, Skorupka E, Dąbrowska G, Polskiego AW. Sarcopenia: monitoring, molecular mechanisms, and physical intervention. Physiological research/Academia Scientiarum Bohemoslovaca. 2014;63(6):683–691. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Lim S, Choi SH, et al. Sarcopenia: an independent predictor of mortality in community-dwelling older Korean men. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014;69(10):1244–1252. - PubMed
-
- Waits SA, Kim EK, Terjimanian MN, et al. Morphometric age and mortality after liver transplant. JAMA surgery. 2014;149(4):335–340. - PubMed
-
- Englesbe MJ, Lee JS, He K, et al. Analytic morphomics, core muscle size, and surgical outcomes. Annals of surgery. 2012;256(2):255–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

