Standardized Outcome Measurement for Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: Consensus From the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM)
- PMID: 25991011
- PMCID: PMC4599409
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.001767
Standardized Outcome Measurement for Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: Consensus From the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM)
Abstract
Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) outcomes consistently improve when they are routinely measured and provided back to physicians and hospitals. However, few centers around the world systematically track outcomes, and no global standards exist. Furthermore, patient-centered outcomes and longitudinal outcomes are under-represented in current assessments.
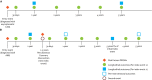
Methods and results: The nonprofit International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM) convened an international Working Group to define a consensus standard set of outcome measures and risk factors for tracking, comparing, and improving the outcomes of CAD care. Members were drawn from 4 continents and 6 countries. Using a modified Delphi method, the ICHOM Working Group defined who should be tracked, what should be measured, and when such measurements should be performed. The ICHOM CAD consensus measures were designed to be relevant for all patients diagnosed with CAD, including those with acute myocardial infarction, angina, and asymptomatic CAD. Thirteen specific outcomes were chosen, including acute complications occurring within 30 days of acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass grafting surgery, or percutaneous coronary intervention; and longitudinal outcomes for up to 5 years for patient-reported health status (Seattle Angina Questionnaire [SAQ-7], elements of Rose Dyspnea Score, and Patient Health Questionnaire [PHQ-2]), cardiovascular hospital admissions, cardiovascular procedures, renal failure, and mortality. Baseline demographic, cardiovascular disease, and comorbidity information is included to improve the interpretability of comparisons.
Conclusions: ICHOM recommends that this set of outcomes and other patient information be measured for all patients with CAD.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; outcomes; patient‐centered.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
References
-
- Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: part I: general considerations, the epidemiologic transition, risk factors, and impact of urbanization. Circulation. 2001;104:2746–2753. - PubMed
-
- 2011. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases. Available at: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd_report2010/en. Accessed April 14, 2014.
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, III, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–e292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, Critchley JA, Labarthe DR, Kottke TE, Giles WH, Capewell S. Explaining the decrease in US deaths from coronary disease, 1980–2000. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2388–2398. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

