Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome without Vestibular Symptoms
- PMID: 25992092
- PMCID: PMC4296991
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1351670
Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome without Vestibular Symptoms
Abstract
Introduction Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome is mainly characterized by vestibular symptoms induced by intense sound stimuli or pressure changes, which occur because of dehiscence of the bony layer covering the superior semicircular canal. Case Report Here, we report a case of the syndrome with pulsatile tinnitus and ear fullness, in the absence of vestibular symptoms. Discussion Signs and symptoms of the syndrome are rarely obvious, leading to the requirement for a minimum workup to rule out or make diagnosis more probable and thus avoid misconduct.
Keywords: ear; inner; semicircular canals; tinnitus.
Figures
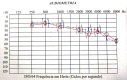

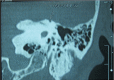

Similar articles
-
Posterior canal dehiscence syndrome caused by an apex cholesteatoma.Otol Neurotol. 2006 Jun;27(4):531-4. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000201433.50122.62. Otol Neurotol. 2006. PMID: 16791045
-
Posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: a morphologic cause of vertigo similar to superior semicircular canal dehiscence.Eur Radiol. 2003 Jun;13(6):1444-50. doi: 10.1007/s00330-003-1828-5. Epub 2003 Feb 15. Eur Radiol. 2003. PMID: 12764665
-
Sound- and/or pressure-induced vertigo due to bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998 Mar;124(3):249-58. doi: 10.1001/archotol.124.3.249. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998. PMID: 9525507
-
Another etiology for vertigo due to idiopathic lateral semicircular canal bony defect.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011 Jun;38(3):402-5. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2010.11.003. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011. PMID: 21216120 Review.
-
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome.J Neurosurg. 2017 Dec;127(6):1268-1276. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.JNS16503. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28084916 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Hearing Loss in a Guinea Pig Model of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence.Neural Plast. 2018 Apr 24;2018:1258341. doi: 10.1155/2018/1258341. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29853836 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Objective Audiovestibular Evaluation of Children With Apparent Semicircular Canal Dehiscence-A Case Series in a Pediatric Vestibular Center.Front Neurol. 2019 Apr 2;10:306. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00306. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31001191 Free PMC article.
-
Audiovestibular Quantification in Rare Third Window Disorders in Children.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 16;11:954. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00954. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33041966 Free PMC article.
-
Third Window Syndrome: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment.J Audiol Otol. 2025 Apr;29(2):86-94. doi: 10.7874/jao.2024.00696. Epub 2025 Apr 18. J Audiol Otol. 2025. PMID: 40296471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minor L B, Solomon D, Zinreich J S, Zee D S. Sound- and/or pressure-induced vertigo due to bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;124:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Carey J P, Minor L B, Nager G T. Dehiscence or thinning of bone overlying the superior semicircular canal in a temporal bone survey. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;126:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Minor L B. Clinical manifestations of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope. 2005;115:1717–1727. - PubMed
-
- Minor L B, Cremer P D, Carey J P, Della Santina C C, Streubel S O, Weg N. Symptoms and signs in superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;942:259–273. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

