Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis as a cause of pulmonary hypertension in adults
- PMID: 25992283
- PMCID: PMC4405719
- DOI: 10.1086/679727
Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis as a cause of pulmonary hypertension in adults
Abstract
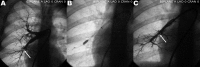
Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis (PPAS) is an underrecognized condition in the adult population. PPAS can lead to pulmonary hypertension but is likely misdiagnosed as either idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. We retrospectively identified adult patients with PPAS either in its isolated form or related to other congenital defects from January 1998 to September 2012. We reviewed the patients' clinical data by using our hospital electronic medical records and/or their paper charts. We identified 6 adult patients with PPAS with an age range of 16-56 years (1 woman and the rest men). Presenting signs and symptoms were thoracic murmurs, progressive dyspnea, and syncope. Three patients had Williams-Beuren syndrome. Pulmonary angiography showed that PPAS was predominantly located in main branches or lobar pulmonary arteries in 5 patients, while in 1 patient the arterial narrowing was at the level of the segmental pulmonary arteries. Right heart catheterization showed a mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) ranging from 35 to 60 mmHg. Balloon dilation was performed in all patients, predominantly in the lobar arteries, and it caused a decrease in mean PAP that ranged from 16% to 46% in 5 patients. In 1 patient the mean PAP did not decrease. All but 1 patient had follow-up echocardiograms at 1 year that showed stable echocardiographic findings. Pulmonary hypertension due to PPAS continues to presents a diagnostic challenge. Therefore, a high index of suspicion during the initial evaluation of pulmonary hypertension is essential for its prompt diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Keywords: diagnosis; peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis; pulmonary hypertension.
Figures

References
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Circulation 2009;119(16):2250–2294. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia, I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62(25 suppl.):D34–D41. - PubMed
-
- Franch RH, Gay BB Jr. Congenital stenosis of the pulmonary artery branches: a classification, with postmortem findings in two cases. Am J Med 1963;35(4):512–529. - PubMed
-
- Gentles TL, Lock JE, Perry SB. High pressure balloon angioplasty for branch pulmonary artery stenosis: early experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;22(3):867–872. - PubMed
-
- Eldredge WJ, Tingelstad JB, Robertson LW, Mauck HP, McCue CM. Observations on the natural history of pulmonary artery coarctations. Circulation 1972;45(2):404–409. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

