Structure-Based Alignment and Consensus Secondary Structures for Three HIV-Related RNA Genomes
- PMID: 25992893
- PMCID: PMC4439019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004230
Structure-Based Alignment and Consensus Secondary Structures for Three HIV-Related RNA Genomes
Abstract
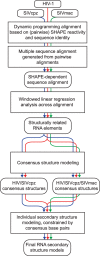
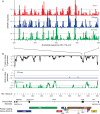
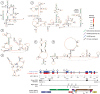
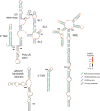
HIV and related primate lentiviruses possess single-stranded RNA genomes. Multiple regions of these genomes participate in critical steps in the viral replication cycle, and the functions of many RNA elements are dependent on the formation of defined structures. The structures of these elements are still not fully understood, and additional functional elements likely exist that have not been identified. In this work, we compared three full-length HIV-related viral genomes: HIV-1NL4-3, SIVcpz, and SIVmac (the latter two strains are progenitors for all HIV-1 and HIV-2 strains, respectively). Model-free RNA structure comparisons were performed using whole-genome structure information experimentally derived from nucleotide-resolution SHAPE reactivities. Consensus secondary structures were constructed for strongly correlated regions by taking into account both SHAPE probing structural data and nucleotide covariation information from structure-based alignments. In these consensus models, all known functional RNA elements were recapitulated with high accuracy. In addition, we identified multiple previously unannotated structural elements in the HIV-1 genome likely to function in translation, splicing and other replication cycle processes; these are compelling targets for future functional analyses. The structure-informed alignment strategy developed here will be broadly useful for efficient RNA motif discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Gesteland RF, Cech T, Atkins JF. The RNA World. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2006.
-
- Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE. Retroviruses. Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE, editors. Cold Spring Harbor (NY)1997.
-
- Muesing MA, Smith DH, Capon DJ. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987;48(4): 691–701. - PubMed
-
- Olsen HS, Nelbock P, Cochrane AW, Rosen CA. Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science. 1990;247(4944): 845–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

